Figure 4.
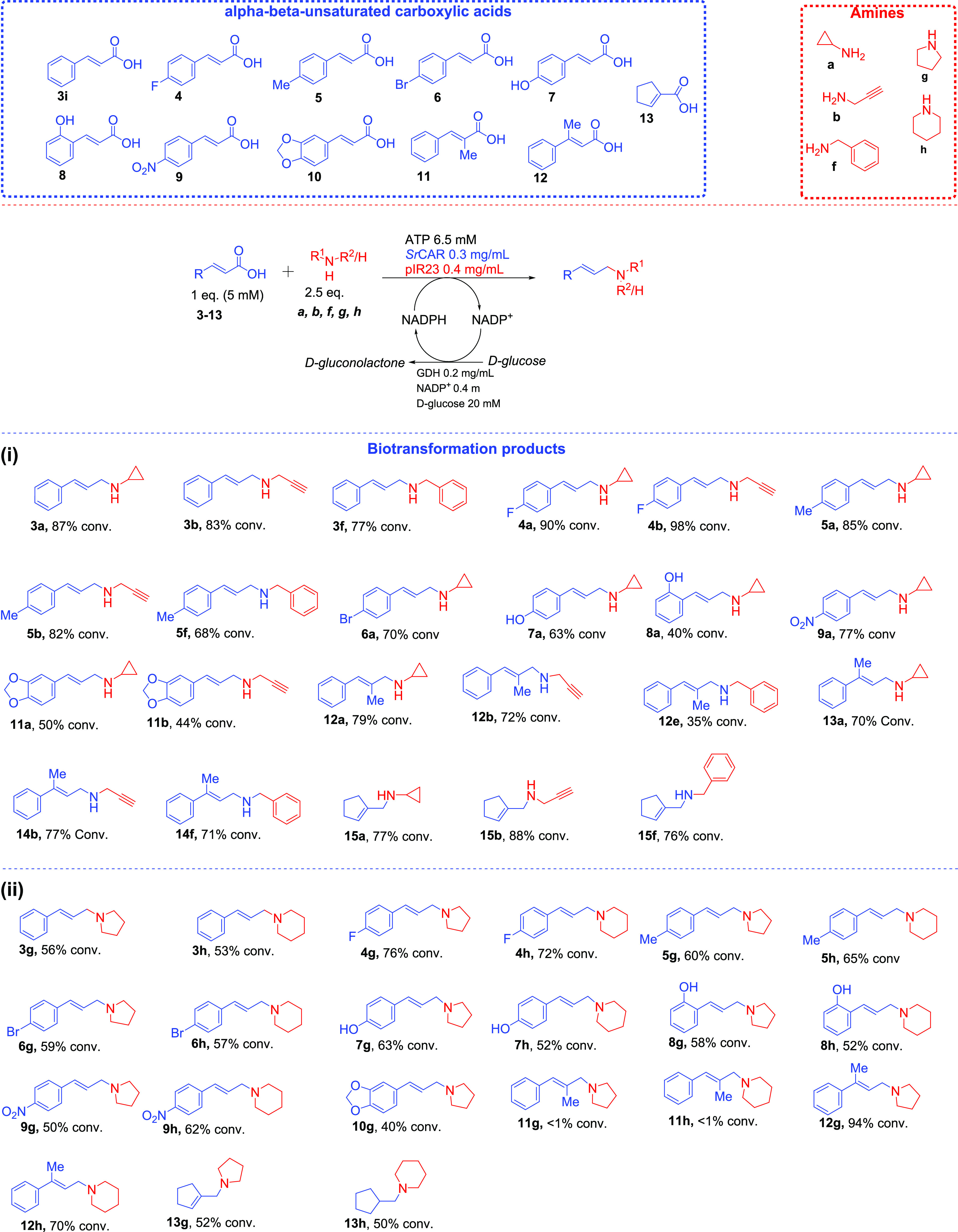
One-pot biocatalytic system for the N-allylation of primary amines and secondary amines with acrylic acid derivatives, generating the corresponding (i) allylic secondary amines and (ii) allylic tertiary amines, respectively. The one-pot two-step system involves an in situSrCAR-catalyzed carboxylate reduction yielding an α,β-unsaturated aldehyde, which is then coupled with a primary or secondary amine in the same pot via pIR23-catalyzed reductive amination. Reaction conditions have been specified in the scheme. Carboxylic acid was used at 5 mM (1 equiv), while amine was supplied at 2.5 equiv. Reactions were performed in NaPi buffer (50 mM, pH 7.5, supplemented with 10 mM MgCl2 and 2% v/v DMSO). Reactions were incubated at 30 °C, 250 rpm for 18 h. For substrates 6, 9, and 10, 1–8% corresponding saturated amine products were detected. Typically, 0.5–15% alcohol product detected. Conversion values were determined from GC-MS analyses. Enzymes: SrCAR = S. rugosus carboxylic acid reductase; GDH = B. subtilis glucose dehydrogenase; and pIR23 = C. ferrugineus reductive aminase. All enzymes were used as purified preparation.
