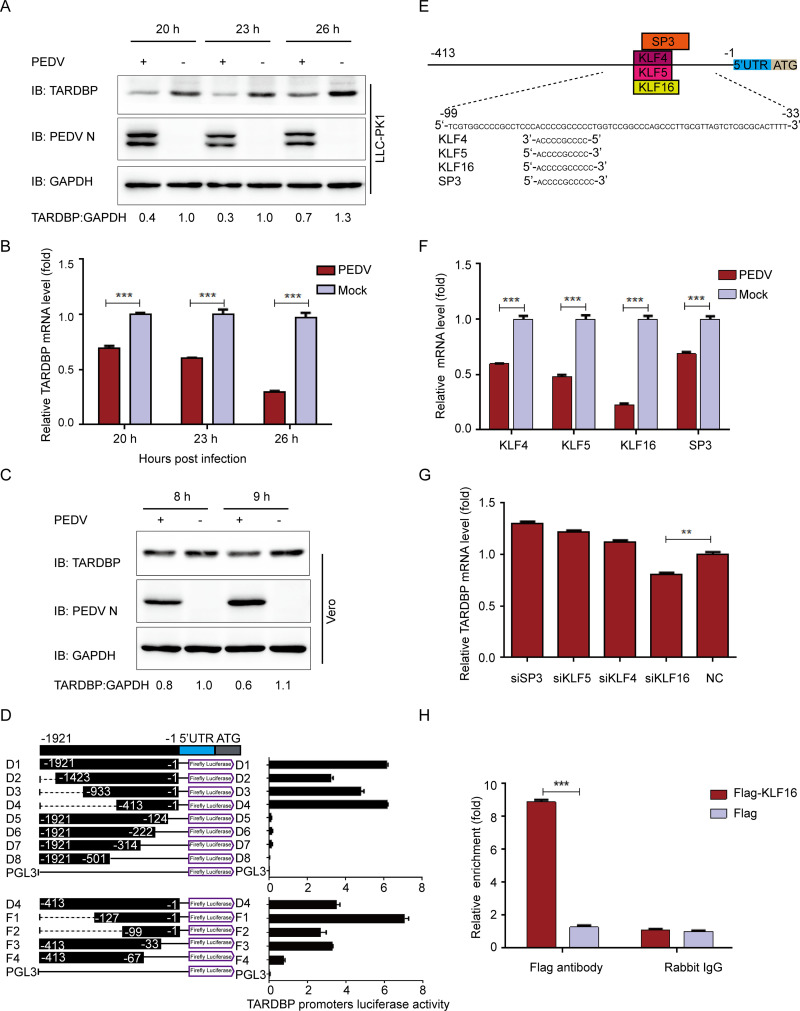
FIG 1.
PEDV infection can inhibit TARDBP expression via transcription factor KLF16. (A) After pseudoinfection or infection of LLC-PK1 cells using PEDV at an MOI of 1, cells were subjected to separate explorations at 20, 23, and 26 hpi. Western blotting was used to analyze the presence of TARDBP and PEDV N proteins. The loading control for samples was ACTB. (B) qRT-PCR was employed for examining the TARDBP mRNA expression in samples identical to those in panel A. (C) After pseudoinfection or infection of Vero cells using PEDV at an MOI of 1, cells were subjected to separate explorations at 8 and 9 hpi. Western blotting was used to analyze the presence of TARDBP and PEDV N proteins. The loading control for samples was ACTB. (D) Cotransfection of HEK 293T cells with a range of truncated constructs (−1921 to −1) of TARDBP promoter was accomplished, where pRL-TK-Luc was utilized for performing dual luciferase experiments. (E) The TFBS of the TARDBP promoter was inspected with JASPAR. (F) Relative mRNAs of predicted genes were explored by qRT-PCR in LLC-PK1 cells infected with PEDV. (G) TARDBP mRNAs in the LLC-PK1 cell-transfected siRNA of predicted genes were studied by qRT-PCR. (H) Following transfection with either Flag-KLF16 plasmid or blank vector, the samples of LLC-PK1 cells were subjected to harvesting and treatment for subsequent ChIP analysis. For the precipitation of chromatin-bound KLF16, a normal rabbit IgG or anti-Flag antibody was utilized. Data presented are means ± SDs from triplicate experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (two-tailed Student's t test).