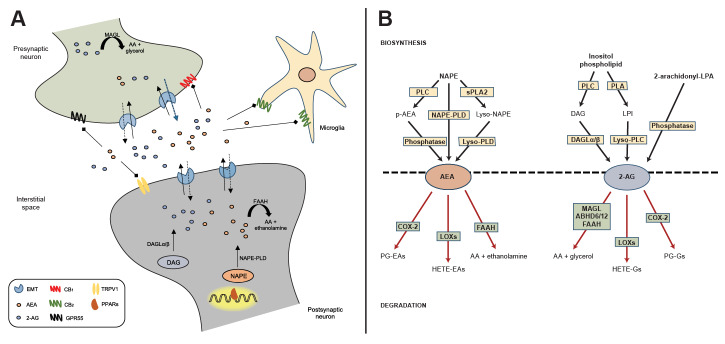
Figure 1. Endocannabinoid signaling and biosynthetic/degradation mechanisms.
A: Schematic representation of the synaptic organization of the main components of the endocannabinoid system, including established routes of AEA and 2-AG metabolism. B: Metabolic pathways of synthesis and degradation of AEA and 2-AG. See text for details. Note: 2-AG, 2-arachidonylglycerol; 2-arachidonoyl-LPA, 2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate; AA, arachidonic acid; ABHD6/12, alpha/beta-hydrolase domains 6 and 12; AEA, anandamide; CB1, cannabinoid receptor type 1; CB2, cannabinoid receptor type 2; COX-2, cyclo-oxygenase 2; DAG, diacylglycerol; DAGLα/β, diacylglycerol lipase-alpha/beta; EMT, endocannabinoid membrane transporter; FAAH, fatty acid amide hydrolase; GPR55, G-protein coupled receptor 55; HETE-EAs, hydroxyeicosatetraenoyl-ethanolamides; HETE-Gs, hydroxyeicosatetraenoyl-glycerols; LOXs, lipoxygenases; LPI, lysophosphatidylinositol; lyso-NAPE, lyso-N-arachidonoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine; lyso-PLC, lyso-phospholipase C; lyso-PLD, lyso-phospholipase D; MAGL, monoacylglycerol lipase; NAPE, N-arachidonoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine; NAPE-PLD, N-arachidonoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D; p-AEA, phospho-anandamide; PG-EAs, prostaglandin-ethanolamides; PG-Gs, prostaglandin-glycerols; PLA, phospholipase A; PLC, phospholipase C; PPARs, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors; sPLA2, soluble phospholipase A2; TRPV1, transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1.