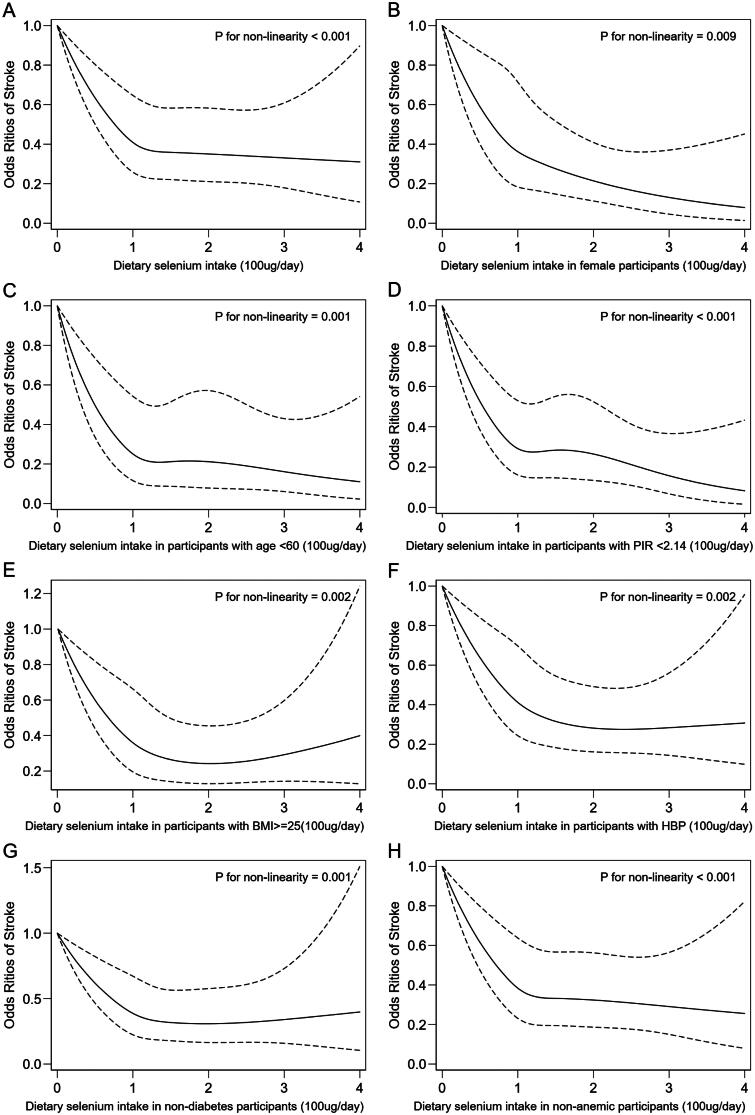
Figure 1.
The weighted odds ratio of stroke correlated with dietary selenium intake. (A) All participants. (B) Female participants. (C) Participants with age <60 years. (D) Participants with PIR <2.14. (E) Participants with overweight and obesity. (F) Participants with hypertension. (G) Participants without diabetes. (H) Participants without anaemia. The solid and long dash lines represent the estimated odds ratio and 95% confidence interval. Odds ratios were adjusted for age, sex, race, education level, marital status, poverty-income ratio, body mass index, smoking, alcohol use, hypertension, diabetes, physical activity, levels of haemoglobin, uric acid, total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, triglyceride, glycohemoglobin, daily intake of total energy and cholesterol from the diet. PIR: family poverty-income ratio.