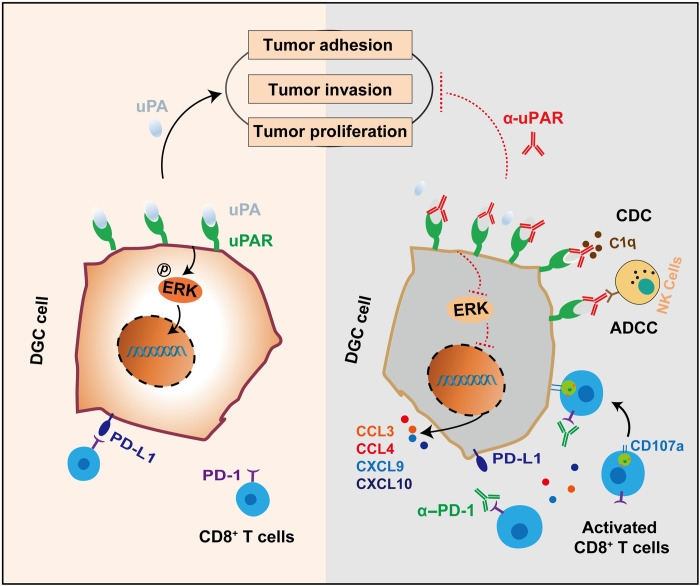
Fig. 7. Therapeutic strategies targeting uPAR potentiate anti–PD-1 efficacy in DGC.
We identify uPAR as an immune-related cell surface protein that is specifically overexpressed in DGC with a relatively high positivity rate and a promising therapeutic potential. Our anti-uPAR mAb targets the DII-DIII region of uPAR and blocks uPA binding to its receptor, thereby inhibiting uPAR-dependent ERK activation and downstream signalings involved in cell proliferation, migration, and adhesion. Moreover, the anti-uPAR mAb stimulates infiltration of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, induces robust ADCC and CDC, and augments the antitumor efficacy of PD-1 blockade therapy.