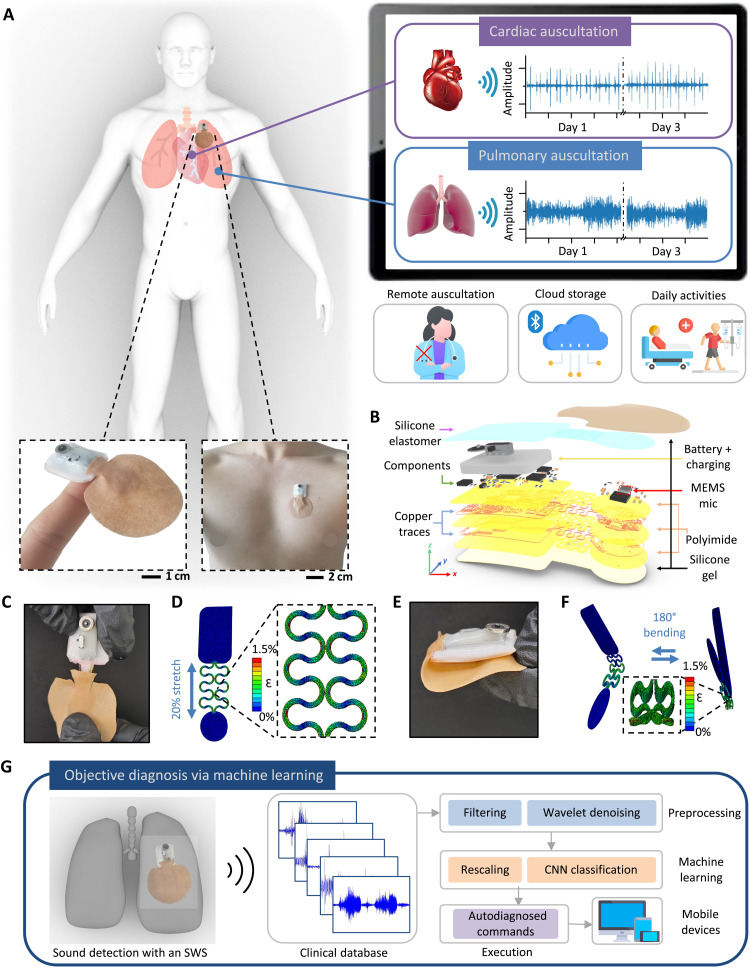
Fig. 1. Design, architecture, and mechanical properties of an SWS.
(A) Schematic illustration of remote monitoring using the SWS, with the zoomed-in photo of the device on the finger and the chest (bottom). Mobile device showing real-time graphs of cardiac and pulmonary auscultation data over 3 days (right) while doing daily activities without any contact (bottom right). (B) Exploded view of the SWS with multiple layers of deposited materials. (C) Image of the 20% stretched interconnects in the SWS. (D) Finite element analysis (FEA) results in (C). (E) Photo of the SWS with 180° bending. (F) FEA results showing cyclic bending from (E). (G) Schematic illustration of the flow for automated, objective diagnosis of diseases via machine learning in the SWS. Various real-time collected abnormal sounds go through preprocessing, machine learning, and classified results stream through the application installed in any mobile device.