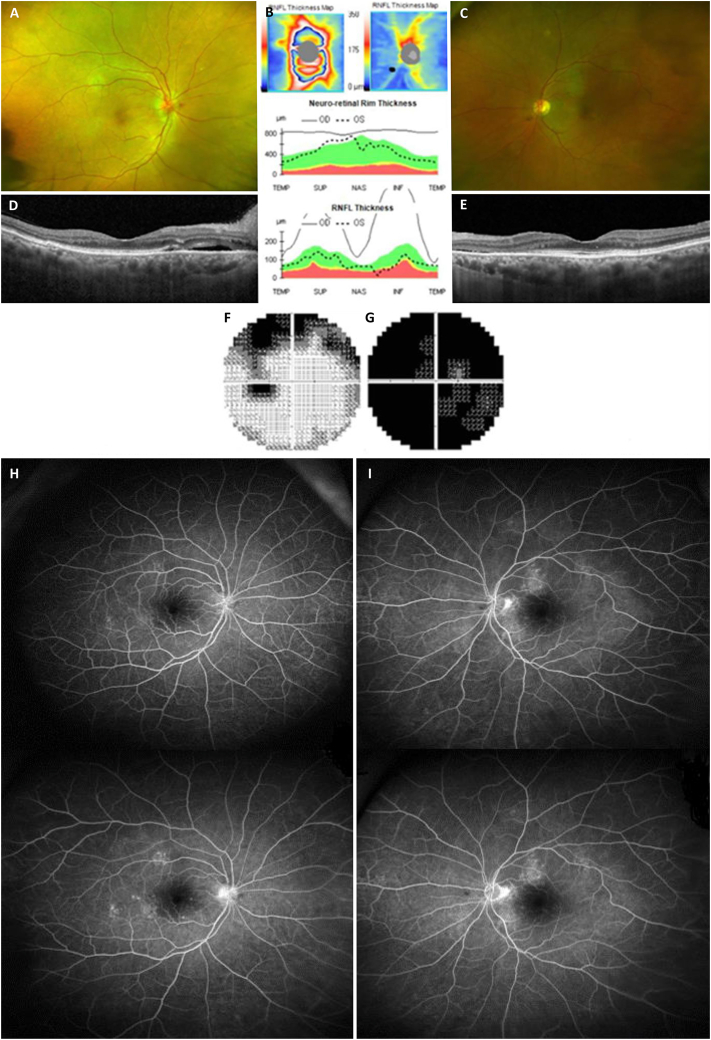
Fig. 1.
Fundus photography (A: right eye, C: left eye) and optical coherence tomography (B: retinal nerve fiver layer thickness and significance map, D: macular cross-sectional image in the right eye, E: macular cross-sectional image in the left eye) revealed optic nerve head swelling in the right eye and subretinal fluid and disruption of the photoreceptor layers in both eyes. The Humphrey field analyzer showed a generalized field defect in the right eye (G) and superior arcuate scotoma in the left eye (F). Fluorescein angiography (H: right eye, I: left eye) showed multiple focal leakages from the retinal vessels without neovascularization at both early (upper images) and late (lower images) phases in both eyes.