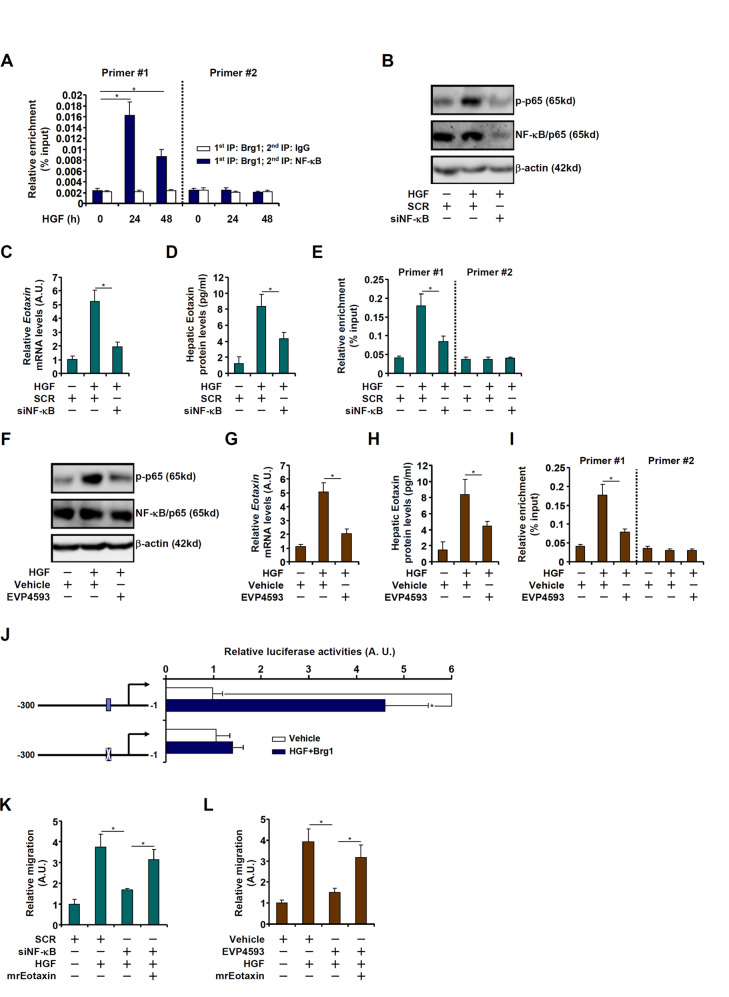
Fig. 5. Brg1 interacts with NF-κB to activate eotaxin transcription.
A Primary murine hepatocytes were treated with HGF (20 ng/ml) and harvested at indicated time points. Re-ChIP assay was performed with indicated antibodies. B–E Primary murine hepatocytes were transfected with siRNA targeting NF-κB or scrambled siRNA followed by treatment with HGF (20 ng/ml). NF-κB expression was examined by Western blotting. Eotaxin expression levels were evaluated by qPCR and ELISA. ChIP assay was performed with anti-Brg1. F–I Primary murine hepatocytes were treated with HGF (20 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of EVP4593 (100 nM). NF-κB expression was examined by Western blotting. Eotaxin expression levels were evaluated by qPCR and ELISA. ChIP assay was performed with anti-Brg1. J WT and NF-κB mutant Eotaxin promoter constructs were co-transfected with a Brg1 expression vector into HepG2 cells followed by treatment with HGF (20 ng/ml) for 24 h. Luciferase activities were normalized by protein concentration and GFP fluorescence. (K) Primary murine hepatocytes were transfected with siRNA targeting NF-κB or scrambled siRNA followed by treatment with HGF (20 ng/ml). Conditioned media were collected and eosinophil migration assay was performed as described in Methods. L Primary murine hepatocytes were treated with HGF (20 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of EVP4593 (100 nM). Conditioned media were collected and eosinophil migration assay was performed as described in Methods. Error bars represent SD (*p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). All experiments were repeated three times and one representative experiment is shown.