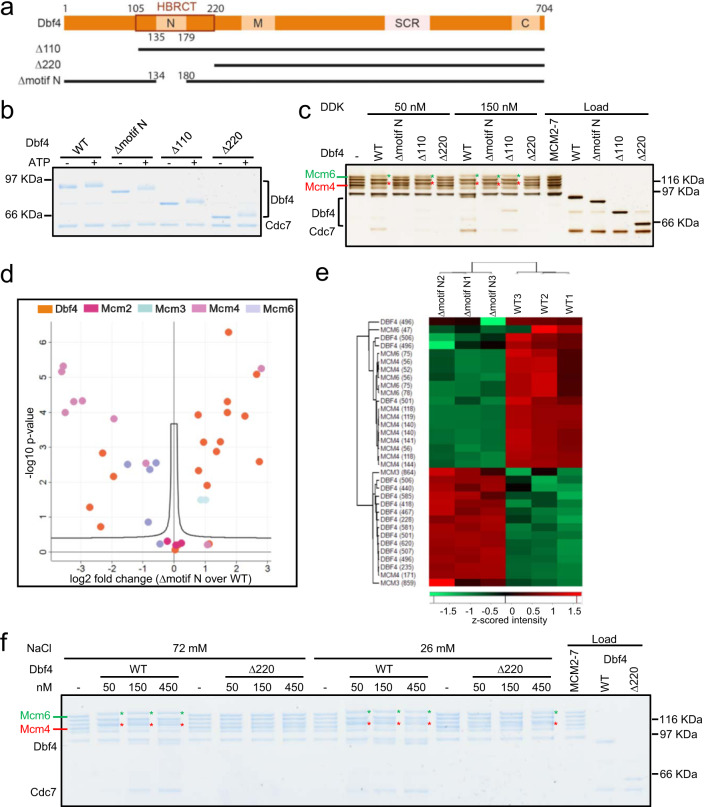
Fig. 2. The Dbf4 N-terminus is important for DDK dependent phosphorylation of MCM2-7.
a Schematic of Dbf4 N-terminal mutants. The Dbf4 regulatory protein features three unique motifs and a modified domain: motif-N, motif-M and motif-C and α-helix-BRCA1 C-terminal (HBRCT) domain. The substrate coordinating region (SCR) is a newly identified domain. b Analysis and comparison of Dbf4-Cdc7 autophosphorylation ability using Dbf4 wild-type and N-terminal mutants. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. c Analysis of Dbf4 N-terminal mutants assessing the interaction of DDK with MCM2-7 DH and MCM2-7 phosphorylation (using 50 and 150 nM DDK concentration). Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. d Volcano plot comparing the DDK phosphorylation profile of the MCM2-7 DH of WT and Δmotif N Dbf4. Two-sample Student’s t-test carried out with three replicate intensities considered per group. P-values were corrected for multiple comparisons to an FDR of 0.05 (permutation-based FDR). e Volcano plot significant phosphosites visualised using Hierarchical Clustering Analysis (HCA) coupled to a heatmap of z-scored site intensities. f Analysis of WT and Δ220 Dbf4 using different protein and salt concentrations. The results highlight that DDK regions within Δ220 Dbf4 do not support binding to the MCM2-7 DH and only very weakly support MCM2-7 phosphorylation activity. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments.