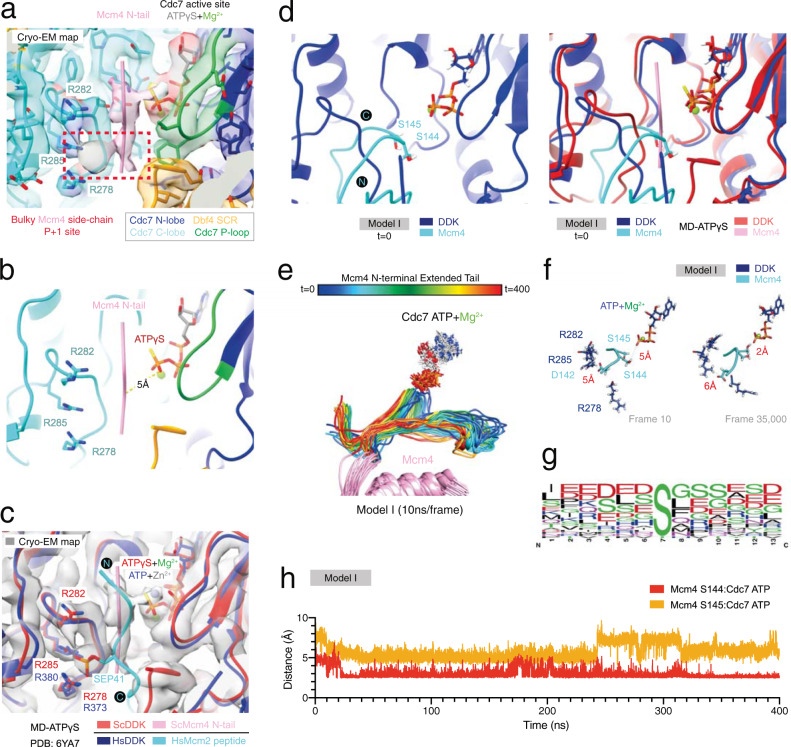
Fig. 8. Molecular dynamics simulation reveals the binding mode of an extended Mcm4 N-terminal tail substrate at the Cdc7 active site.
a Zoomed view of the MD-(ATPγS) state III atomic model DDK active site and associated cryo-EM density map. The cryo-EM map features density reminiscent of a bulky Mcm4 tail residue side chain at the P + 1 site. This Mcm4 tail unknown residue is also surrounded by Cdc7 R278, R282 and R285. b Simplified view of (a) displaying the distance measurement between the Mcm4 N-terminal tail (backbone CA atom) and Cdc7 ATPγS (O3G atom). c Overlay of the core of human DDK (PDB:6YA7) and budding yeast DDK atomic models. The position of the phospho-serine residue (SEP) in the human Mcm2 peptide matches with the bulky residue side chain density position observed in the MD-(ATPγS) cryo-EM map. d Zoomed view of the DDK active site of Model I (molecular dynamics starting model I, featuring an extended Mcm4 N-terminal tail) and comparison with the MD-(ATPγS) atomic model. e Snapshots of model trajectory, sampled every 10 ns, during a 400 ns GROMACS molecular dynamics simulation. The successive order of the models is represented by rainbow colours (red to blue). The long flexible Mcm4 tail adopts multiple conformations throughout the simulation. f Simplified view of the DDK active site, showing the distance measurements between the nearest DDK Mcm4 target residue (S144, OG atom) and Cdc7 ATPγS (O3G atom) and Mcm4 D142 (CG atom) at the P-2 position and R285 (NE atom). g Sequence logo, generated using WebLogo 3, displaying the frequency (N) of different amino acid residues at atypical human DDK target sites1. The residues preceding the target DDK residue feature in a high proportion of cases acidic residues (D/E). h Plot of distance measurement between the Mcm4 N-terminal tail (backbone CA atom) and Cdc7 ATPγS (O3G atom) throughout the entire simulation.