Figure 2. RagA-RagC(F92A) preferentially binds GATOR1 in the GAP mode.
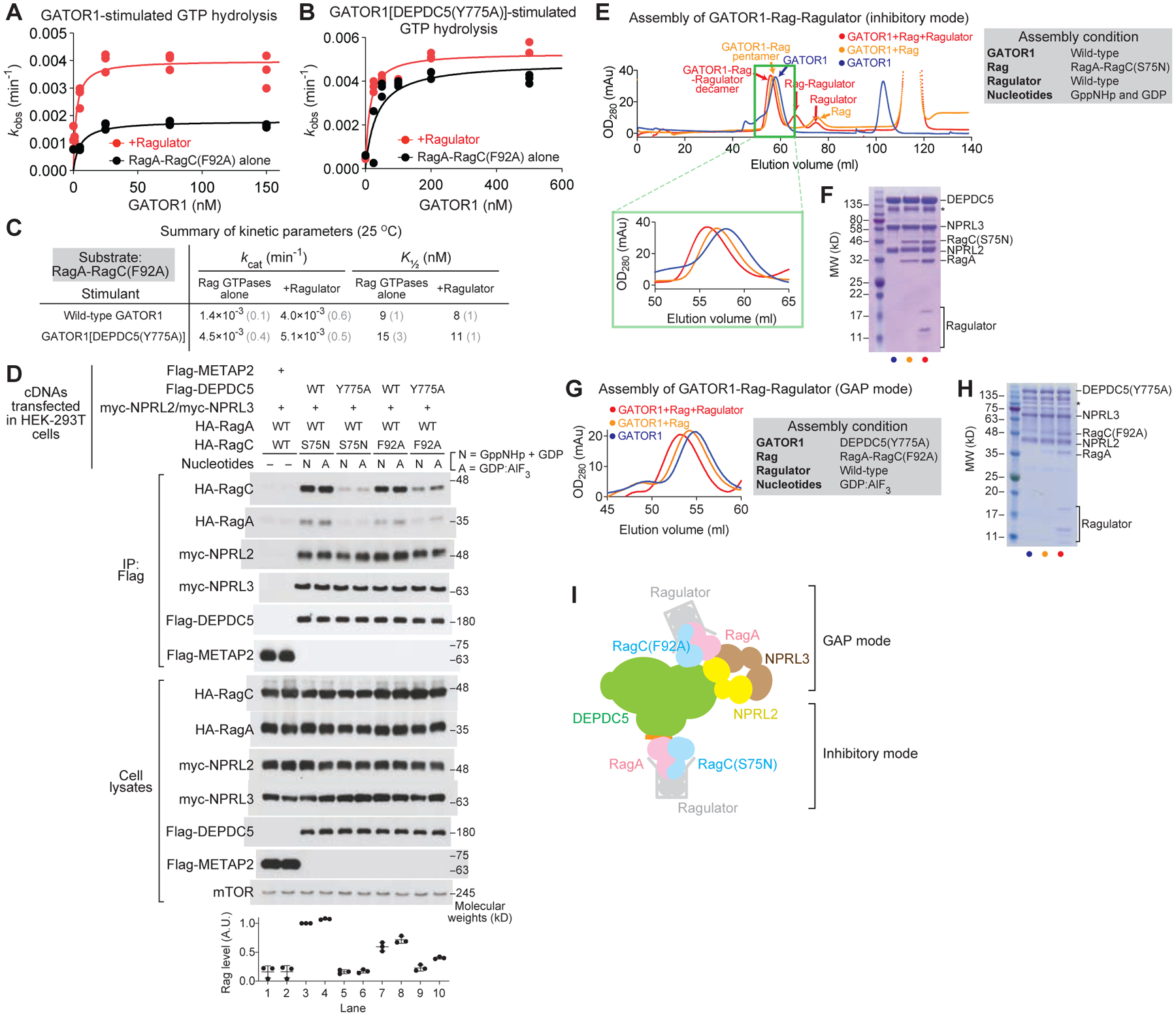
A & B. Stimulated GTP hydrolysis by RagA-RagC(F92A) in the presence or absence of Ragulator, with wild-type GATOR1 (A) or GATOR1[DEPDC5(Y775A)] (B) as stimulant.
C. Summary of kinetic parameters from panels A and B. Gray numbers in parentheses denote the SEMs of the reported values calculated from three independent experiments.
D. In vivo binding assay between GATOR1 and the Rag GTPases.
E. Gel-filtration profiles for the assembly of the GATOR1-Rag-Ragulator complex in the inhibitory mode.
F. Coomassie staining gel for the eluate at high molecular weight region. Subunits of GATOR1, RagA-RagC(S75N), and Ragulator can be visualized. Asterisk denotes a non-specific band commonly observed in GATOR1 purification.
G. Gel-filtration profiles for the assembly of the GATOR1-Rag-Ragulator complex in the GAP mode.
H. Coomassie staining gel for the eluate at high molecular weight region. Subunits of GATOR1[DEPDC5(Y775A)], RagA-RagC(F92A), and Ragulator can be visualized. Asterisk denotes non-specific bands commonly observed in GATOR1 purification.
I. Scheme for the binding between GATOR1 and Rag-Ragulator.
