Figure 4. Architecture of the GATOR1-Rag-Ragulator complex.
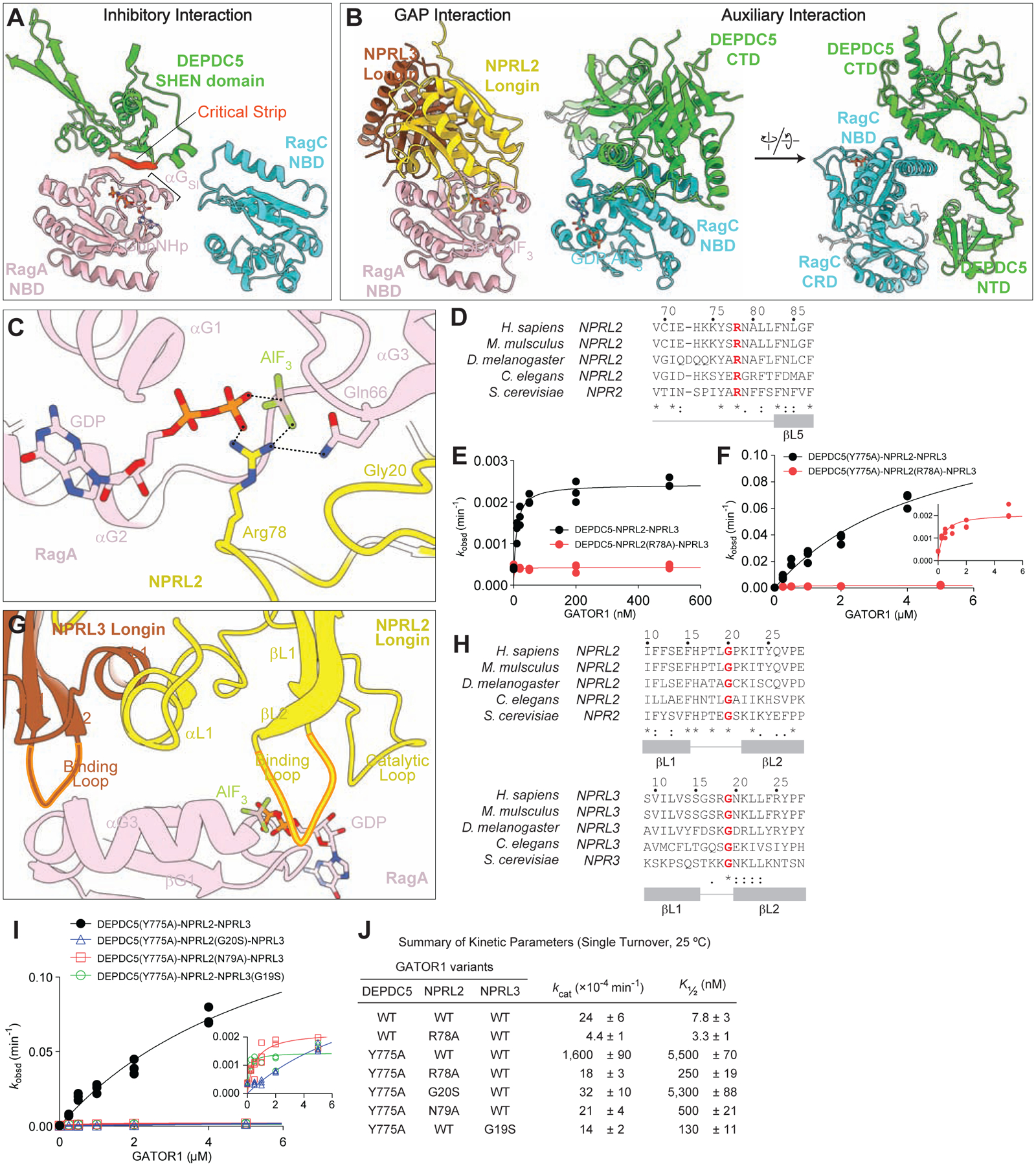
A. Interaction between the Rag GTPase heterodimer and GATOR1 in the inhibitory mode.
B. Interaction between the Rag GTPase heterodimer and GATOR1 in the GAP mode.
C. Arg78 of NPRL2 points at the nucleotide bound to RagA, serving as an arginine finger to catalyze GTP hydrolysis by RagA.
D. Sequence conservation of Arg78 across species.
E. Stimulated GTP hydrolysis assay by GATOR1 containing NPRL2(R78A) mutation.
F. Stimulated GTP hydrolysis assay by GATOR1 containing DEPDC5(Y775A) and NPRL2(R78A) mutations.
G. Two loops on NPRL2 and NPRL3 coordinate the binding to RagA-NBD.
H. Sequence conservation of the two loops on NPRL2 and NPRL3.
I. Stimulated GTP hydrolysis assay by GATOR1 containing mutations on the loop of NPRL2 and NPRL3 (inset shows zoom-in of NPRL2 and NPRL3 mutants).
J. Summary of kinetic parameters from panels 4E, 4F, and 4I. Mean ± SEMs from three independent experiments are reported.
