Figure 5. DEPDC5 coordinates the nucleotide loading states of RagA and RagC.
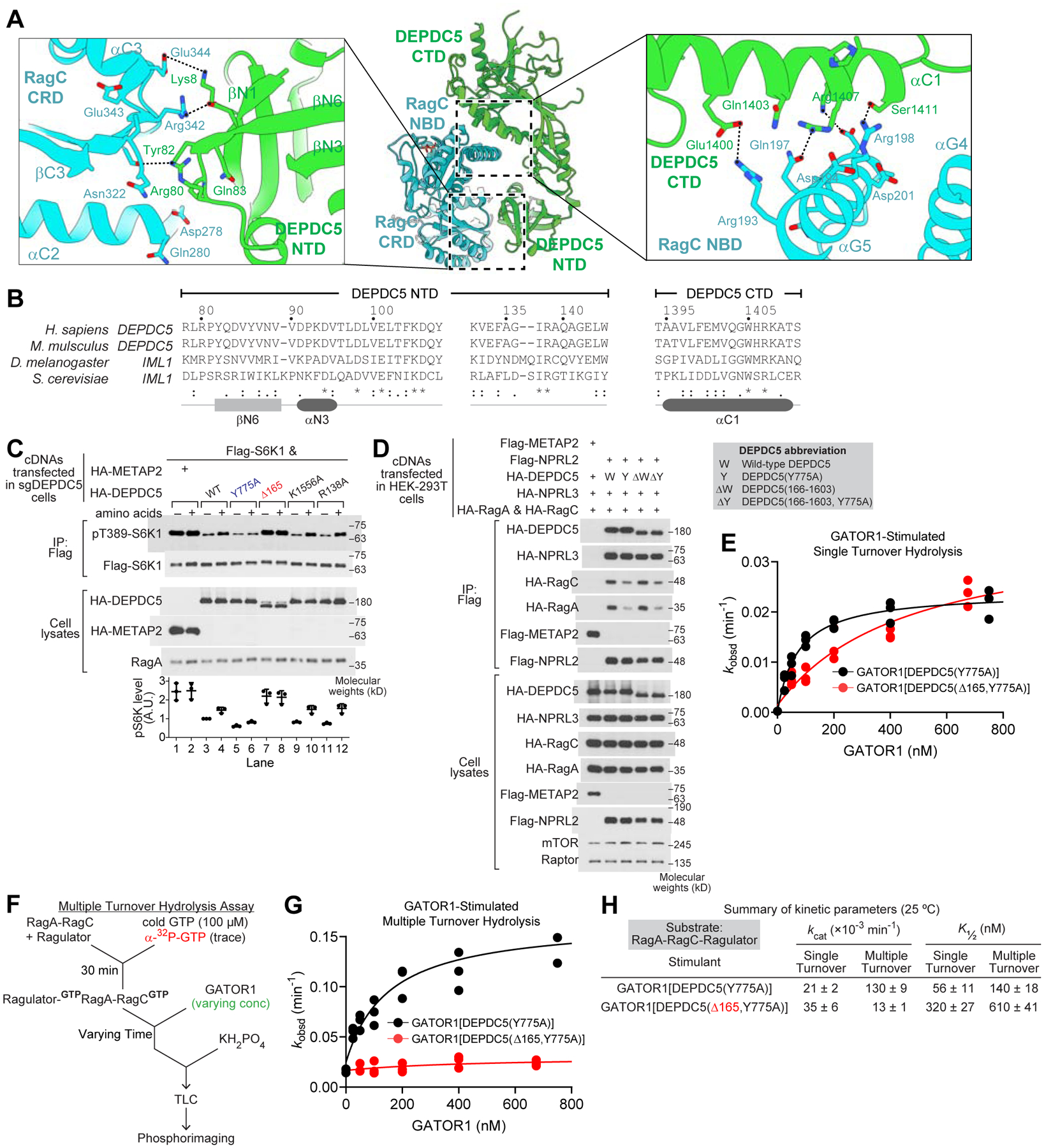
A. Interaction between DEPDC5 and the RagC subunit is mediated by two contact surfaces: the RagC C-terminal roadblock domain (CRD) and DEPDC5 N-terminal domain (NTD, left), as well as the RagC nucleotide binding domain (NBD) and DEPDC5 C-terminal domain (CTD, right).
B. Sequence conservation of DEPDC5-NTD and DEPDC5-CTD.
C. Effect of expression of various DEPDC5 mutants on the ability of sgDEPDC5 cells to restore mTORC1 signaling in the presence and absence of amino acids.
D. Co-immunoprecipitation of NPRL2, NPRL3, and the Rag GTPase heterodimer with the DEPDC5 variants.
E. Single turnover GTP hydrolysis assay by GATOR1 containing DEPDC5(Δ165) mutation.
F. Experimental setup for the multiple turnover GTP hydrolysis assay.
G. Multiple turnover GTP hydrolysis assay stimulated by GATOR1 containing DEPDC5(Δ165, Y775A) mutation.
H. Summary of GTP hydrolysis kinetics for Rag-Ragulator under single- and multiple-turnover conditions at 25 °C. Mean ± SEMs from three independent experiments are reported.
