Figure 3.
Cynomolgus macaque CAR T cells demonstrate antigen-specific suppressor function
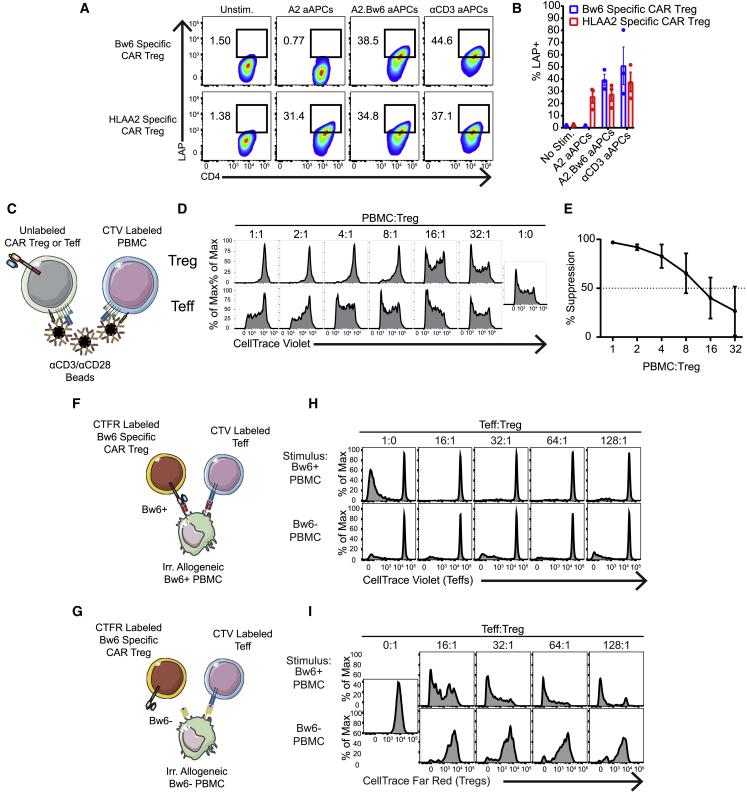
(A and B) Bw6- or HLA-A2-specific CAR Tregs were co-cultured with the indicated aAPC for 24 h and then stained for LAP expression (n = 3 independent experiments).
(C) Antigen non-specific suppression was measured by co-culture of unlabeled Bw6-specific CAR Tregs or Bw6-specific CAR Teffs with CellTrace Violet (CTV)-labeled allogeneic PBMCs and α-CD3/α-CD28 beads at the indicated PBMC:Treg ratio for 4 to 5 days.
(D) Histograms depict proliferation of the CD4− CD8+ CTV+ cells present in the allogenic PBMCs of experiment performed as depicted in (C).
(E) Line graph representing mean ± SEM of seven independent experiments performed as in (D).
(F and G) Antigen specific suppression was assessed by mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR). CTV-labeled responder Teffs and CellTrace Far Red (CTFR)-labeled, Bw6-specific CAR T cells were co-cultured with unlabeled, irradiated allogeneic PBMCs from either Bw6+ or Bw6− animals.
(H) Histograms showing proliferation of the CD4− CD8+ CTV+ Teffs in the MLR performed as depicted in (F) and (G).
(I) Histograms showing proliferation of CD4+ CTV− CTFR+ Bw6-specific Tregs in same MLR wells as (H). MLRs were assessed between seven pairs of animals in two independent experiments, and similar data were obtained in both experiments.