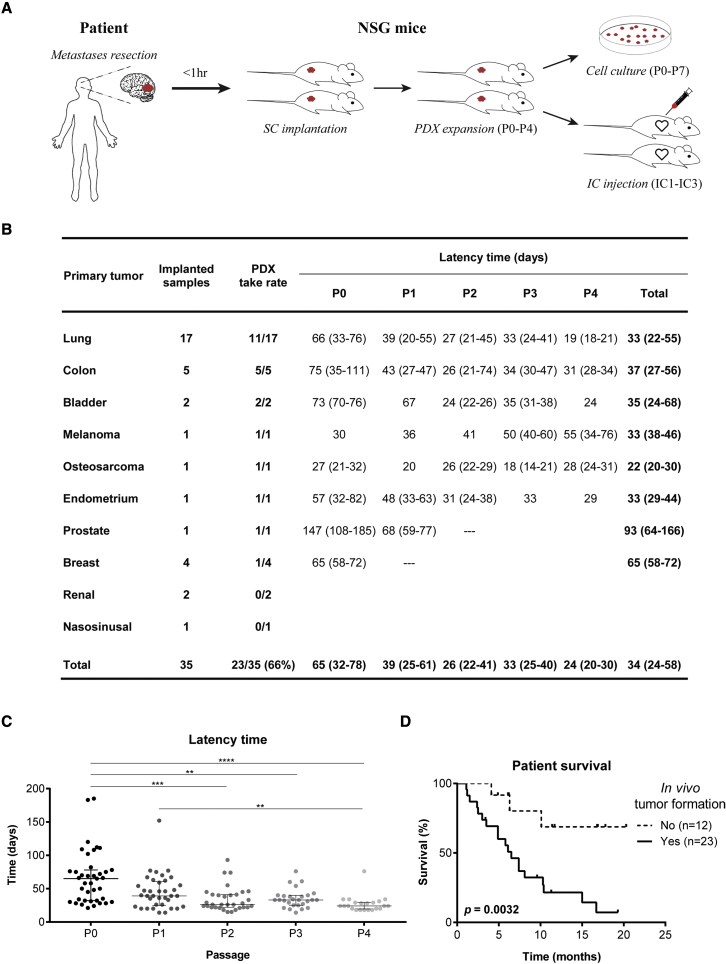
Figure 1.
Subcutaneous xenografts derived from BM surgical samples
(A) Experimental workflow for patient-derived models. Samples were implanted in the flank of immuno-compromised NSG mice and serially expanded until passage four. Flank tumors were dissociated into single cell suspensions that were used to establish PDCs up to passage seven, or to perform intracardiac injection in the left cardiac ventricle of NSG mice (up to three serial injections).
(B) Take rate and latency time of subcutaneously implanted human BMs from diverse primary cancers.
(C) Tumor latency time decreases upon in vivo serial passaging (n = 2 NSG mice/passage for each engrafted BM sample).
(D) The in vivo tumorigenic potential of BM surgical samples correlates with patient poor survival. Data are expressed as median with interquartile range. Differences were considered statistically significant for p values <0.05, according to the Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparisons and Log rank (Mantel-Cox) tests. See also Table S1, Figures S1 and S2.