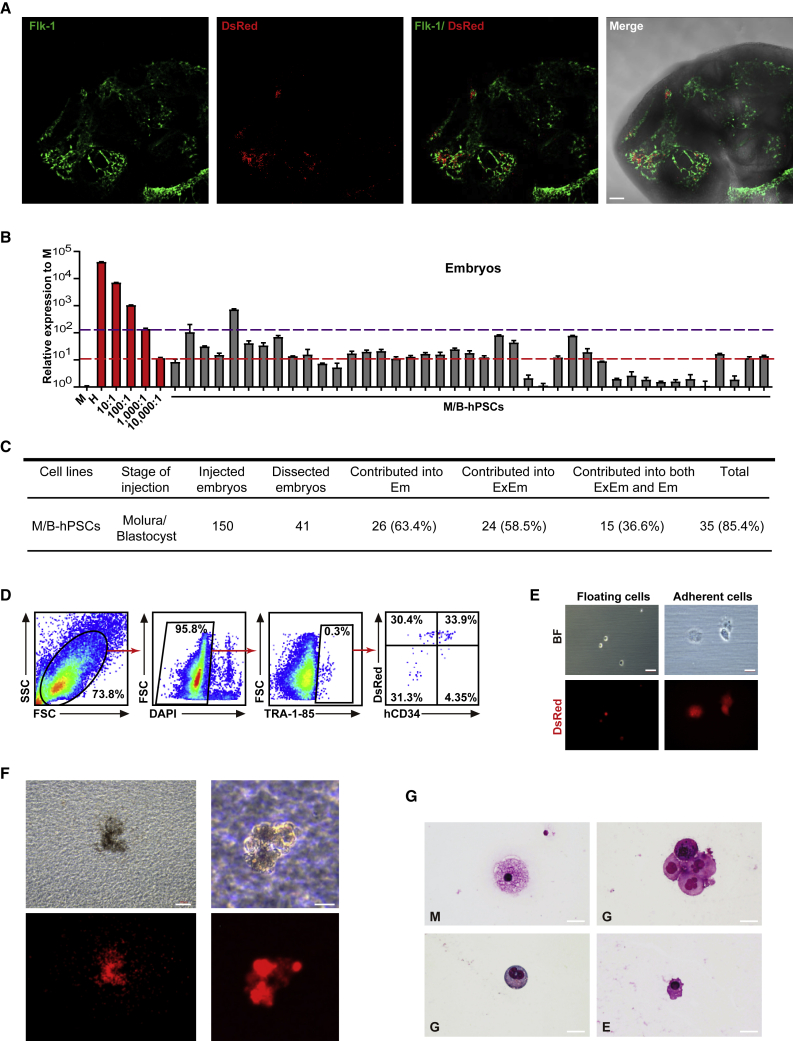
Figure 4.
Generation of human CD34+ endothelial/blood progenitor cells through interspecies chimera
(A) Representative fluorescence images showing the integration of human cells in the vascular regions of E10.5 Flk-1+/EGFP mouse chimeric embryos. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(B) Quantitative genomic PCR analysis of the human mitochondria DNA in E10.5 Flk-1+/EGFP mouse chimeras injected with M/B-hPSCs. A human DNA control (H), a mouse DNA control (M), and a series of human-mouse cell dilutions (1/100 to 1/100,000) were run in parallel to estimate the degree of human cell integration. The red and purple dashed lines indicate the detection level of one human cell in 10,000 and 1,000 mouse cells, respectively. Error bars represent mean + SEM of three parallel experiments.
(C) Summary of mouse chimeras containing human cells. Embryos were recovered and analyzed at the E10.5 stage. ExEm, extra-embryonic tissues including both placentas and yolk sacs; Em, embryonic lineages.
(D) Representative flow cytometry analysis of live human cells in E10.5 Flk-1+/EGFP mouse chimeric embryos. The antibody TRA-1-85 was used to identify human cells, and hCD34 was used to identify human endothelial and blood cells.
(E) The morphology of sorted live human cells (TRA-1-85+). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(F) Representative pictures of CFUs formed by the sorted live human cells (TRA-1-85+dsRed+). To sort the cells for CFU assay, total cells from 10 embryos were pooled together, and roughly around 2,000 human TRA-1-85+dsRed+ cells were obtained. Around 1,000 human cells were seeded, and a total of 5 CFUs were detected. Scale bars, 200 μm (left) and 100 μm (right).
(G) May–Grunwald–Giemsa staining of different blood cells from (F). Scale bars, 20 μm. E, erythroid; G, granulocytes; M, macrophages.