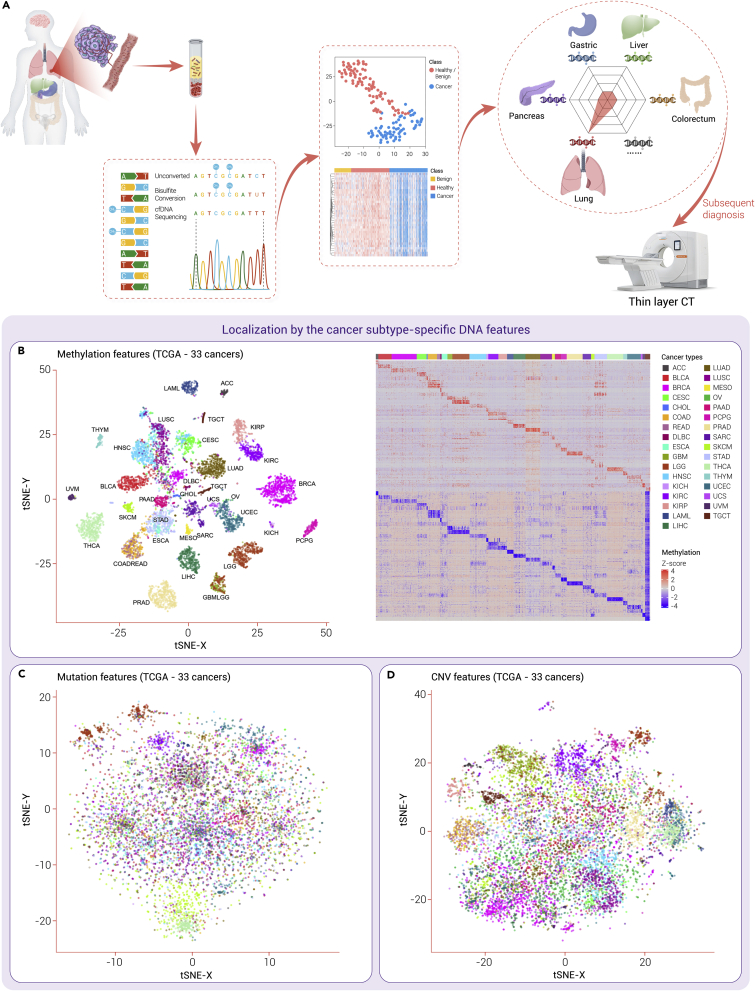
Figure 3.
Comparison of the tissue-of-origin efficacy of methylation, mutation, and CNV features
(A) Take lung cancer as an example. The cfDNA released from lung tissue is increased in the plasma owing to the lung injury caused by tumor compression and invasion, and this increase could be detected by mapping the sequencing data to the profiles of different tissues. Then lung cancer is suspected, and a subsequent LDCT is subjected to the patient for further diagnosis. (B–D) We performed t-SNE to decrease the dimensionality of methylation, mutation, and copy number data of the 33 cancer types in TCGA database. Particularly, a heatmap of methylation data shows the cancer subtype-specific hypomethylated and hypermethylated regions. ACC, adrenocortical carcinoma; BLCA, bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA, breast invasive carcinoma; CESC, cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma; CHOL, cholangiocarcinoma; CNV, copy number variation; COAD, colon adenocarcinoma; DLBC, lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; ESCA, esophageal carcinoma; GBM, glioblastoma multiforme; HNSC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; KICH, kidney chromophobe; KIRC, kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; KIRP, kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; LAML, acute myeloid leukemia; LGG, brain lower grade glioma; LIHC, liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, lung squamous cell carcinoma; MESO, mesothelioma; OV, ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma; PAAD, pancreatic adenocarcinoma; PCPG, pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma; PRAD, prostate adenocarcinoma; READ, rectum adenocarcinoma; SARC, sarcoma; SKCM, skin cutaneous melanoma; STAD, stomach adenocarcinoma; t-SNE, t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding.; TGCT, testicular germ cell tumors; THCA, thyroid carcinoma; THYM, thymoma; UCEC, uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma; UCS, uterine carcinosarcoma.