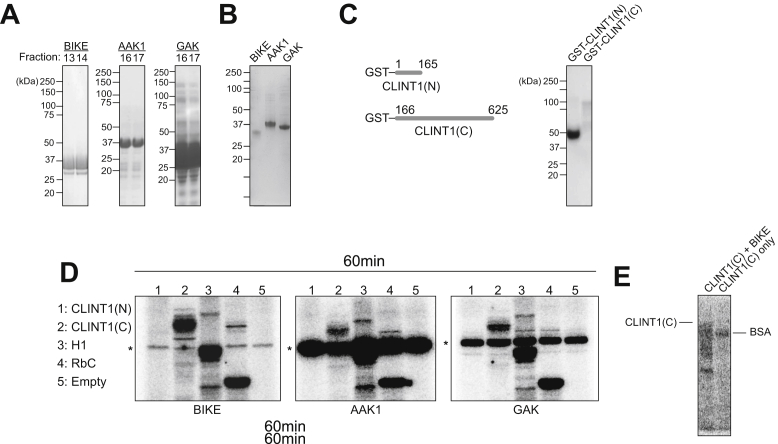
Figure 3.
BIKE phosphorylates CLINT1 in vitro. A, rBIKE, rAAK1, and rGAK purified by gel filtration. Representative fractions are shown. Membranes were blotted with the respective anti-NAK antibodies. B, Coomassie-stained rBIKE, rAAK1, and rGAK ran on an SDS-PAGE gel. C, left: Schematics showing recombinant GST-tagged N- and C-terminal CLINT1 fragments (CLINT1(N) and CLINT1(C)) purified from bacterial cells. Right: rCLINT1(C) and rCLINT1(N) by GST pulldown following expression in bacterial cells. D, autoradiographs from in vitro kinase assays carried out by incubating recombinant BIKE, AAK1, or GAK kinases with CLINT1(N), CLINT1(C), H1, RbC, or no substrate. After 60 min, reactions were stopped with SDS sample buffer. E, autoradiograph results from in vitro kinase assay carried out by incubating rCLINT1(C) in the presence or absence of rBIKE and ATP for 60 min followed by reaction termination via addition of SDS sample buffer. Molecular weight markers are indicated on the left (kDa). AAK1, adapter-associated kinase 1; BIKE, BMP2-inducible kinase; CLINT1, clathrin-interacting protein 1; GAK, G-cyclin–associated kinase.