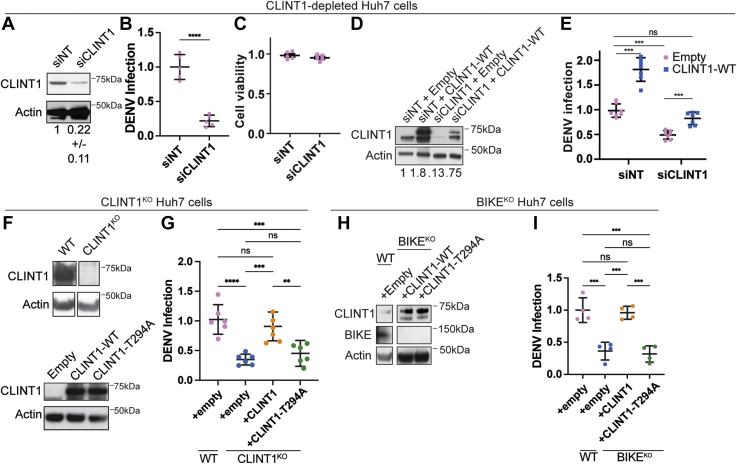
Figure 5.
CLINT1 is required for DENV infection and is involved in mediating the role of BIKE in DENV infection. A–I, CLINT1 protein by Western blot in Huh7 cells depleted of CLINT1 via siRNA or NT controls (A and D) or deleted for CLINT1 (F) or BIKE (H) via CRISPR/Cas9 and in these cells upon complementation with FLAG-tagged WT or T294A CLINT1 mutant and an empty plasmid (D, F and H). Representative membranes blotted with anti-CLINT1, anti-BIKE, and anti-actin antibodies and quantitative CLINT1 to actin ratios are shown. Samples were run on the same gels (F and H), from which several lanes were cut out. DENV infection (B, E, G and I) and cell viability (C) as measured in the indicated cells by luciferase and alamarBlue assays, respectively, at 48 h postinoculation with luciferase reporter DENV2 (MOI=0.05). Shown in B, C, and I are mean ± SD of results of representative experiments out of at least two conducted, each with 4 or 5 replicates. Shown in E and G are mean SEM of data combined from two independent experiments with 3 or 4 replicates each. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001 relative to corresponding controls by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s (B and C) or Tukey’s (E, G and I) post hoc tests. BIKE, BMP2-inducible kinase; CLINT1, clathrin-interacting protein 1; DENV, dengue virus; MOI, multiplicity of infection; ns, nonsignificant.