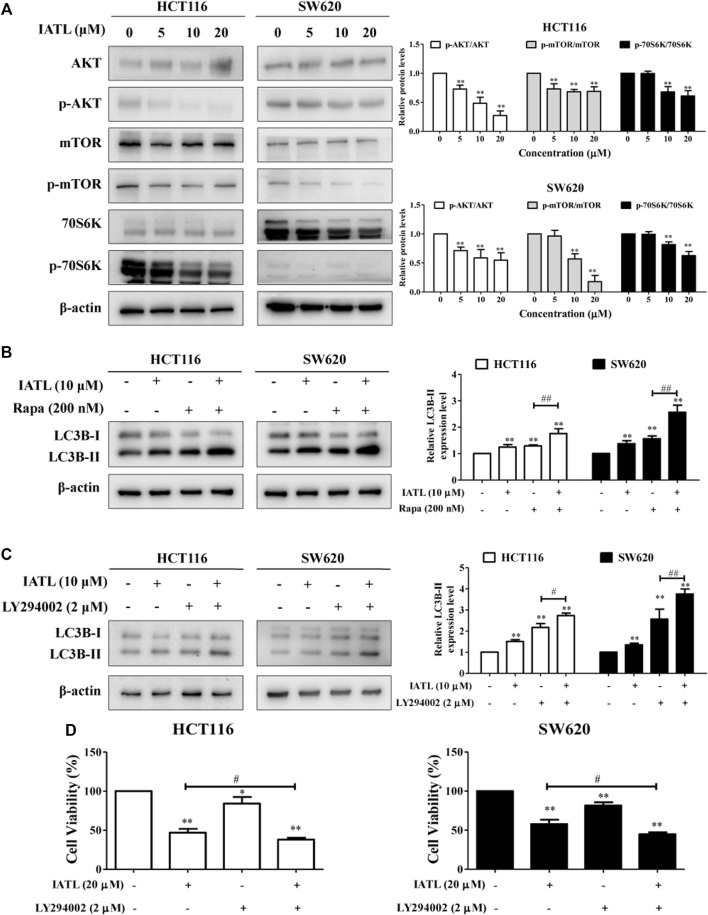
FIGURE 6.
Inhibiting AKT/mTOR signaling contributes to IATL-induced autophagy in CRC cells. HCT116 and SW620 cells were treated with indicated drugs for 24 h (A) IATL inhibited AKT/mTOR signaling in CRC cells. Cells were treated with various concentrations of IATL for 24 h. (B) Effects of IATL on LC3B-II protein level in the absence or presence of Rapa (100 nM, an mTOR inhibitor) in CRC cells. (C) Effects of IATL on LC3B-II protein level in the absence or presence of LY294002 (2 μM, an AKT/mTOR signaling inhibitor) in CRC cells. Protein levels were examined by immunoblotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. Representative immunoblotting bands are presented in left panels, and quantitative results are shown in right panels. (D) CRC cells were treated with IATL (20 μM) in the presence or absence of LY294002 (2 μM) for 24 h. Cell viability was assessed using MTT assays. Data in bar charts are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. vehicle control. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01.