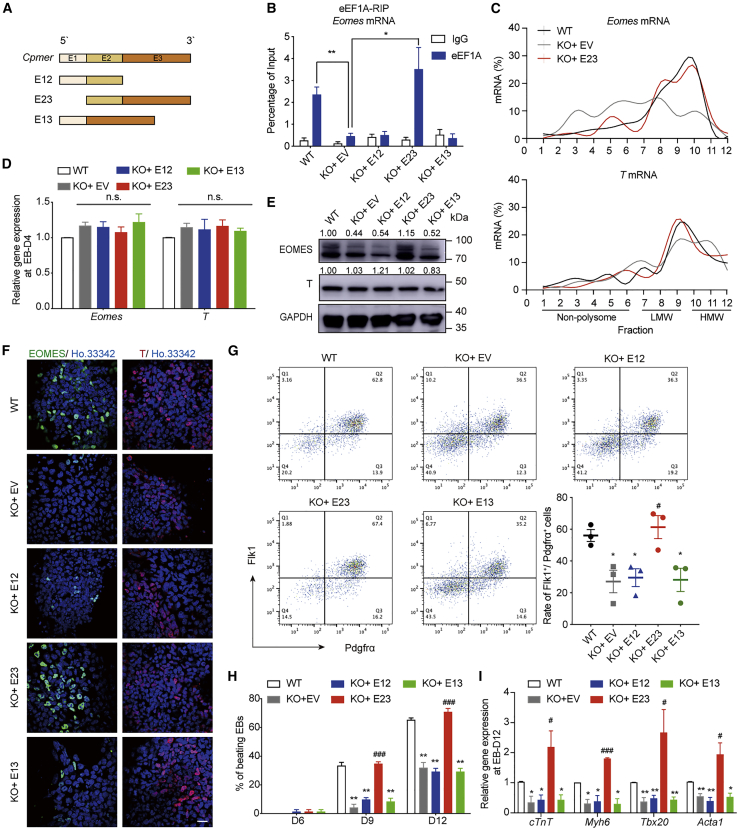
Figure 5.
E23 of Cpmer is responsible for Eomes translation and CM differentiation
(A) Schematic of Cpmer mutants.
(B) RIP analysis of eEF1A binding with Eomes mRNA in KO-Cpmer cells transfected with Cpmer mutants. Data shown are the mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments.
(C) Polysome profile analysis of Eomes and T mRNAs.
(D–F) qRT-PCR (D), western blot (E), and immunofluorescence (F) detection of expression of Eomes and T. Data shown are the mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(G) Representative FACS results and the statistics of percentage of Flk1+Pdgfrα+ cells. Data shown are the mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments.
(H) Percentage of spontaneously contracting EBs. Data shown are the mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments.
(I) qRT-PCR analysis of the CM marker genes. Data shown are the mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 (versus the WT); #p < 0.05 and ###p < 0.001 (versus KO + EV [empty vector]); Student’s t test.
See also Figure S5.