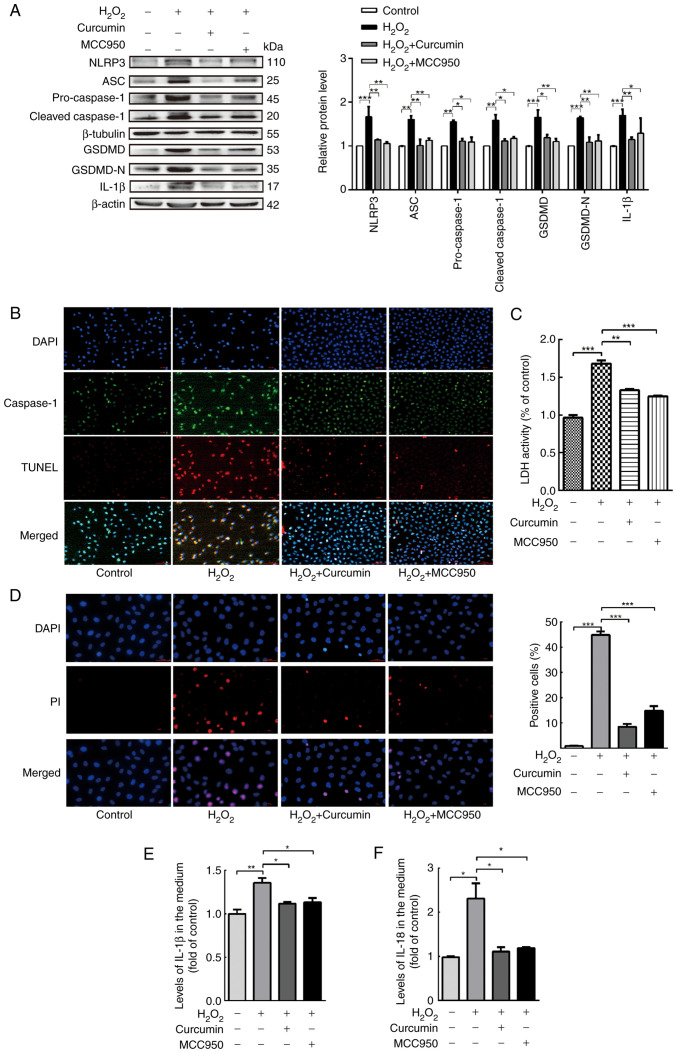
Figure 4.
Curcumin alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome activation, which is involved in pyroptosis. HUVECs were treated with H2O2 for 3 h and then either treated with 25 µM curcumin for 3 h or left untreated (control), whereas for the MCC95 group, HUVECs were pretreated with NLRP3 inhibitor (MCC950; 10 µM) for 2 h and then incubated with H2O2 (800 µM) for 3 h. (A) Western blot analysis indicated that the protein levels of NLRP3, ASC, pro-caspase-1, caspase-1, pro-GSDMD, GSDMD and IL-1β were upregulated in HUVECs following treatment with H2O2 for 3 h and that MCC950 and curcumin inhibited the protein expression of NLRP3, ASC, pro-caspase-1, caspase-1, pro-GSDMD, GSDMD and IL-1β. β-Actin or β-tubulin was used as an internal control. (B) As compared with the H2O2 group, caspase-1 (green) and TUNEL (red) double-positive cells were decreased in the presence of curcumin or MCC950. The nuclei were stained blue with DAPI (magnification, ×400; scale bar, 50 µm). (C) The relative release of LDH by H2O2-treated HUVECs was increased, while that of curcumin- and MCC950-treated HUVECs was decreased (n=3). (D) The percentage of PI (red)-positive H2O2-treated HUVECs was increased, while that among curcumin- and MCC950-treated cells was decreased (left, representative images; right, quantification of PI-positive cells) (magnification, ×400; scale bar, 50 µm). Relative concentration of (E) IL-1β and (F) IL-18 in the culture medium following H2O2, curcumin or MCC950 treatment of HUVECs, as determined by ELISA. Values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; NLRP3, NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3; GSDMD, gasdermin D; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PI, propidium iodide.