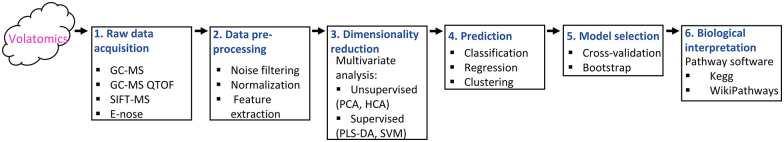
Figure 7.
Workflow for volatomic analysis. First, measuring devices are needed (eg, GC-MC, GC-MS QTOF, SIFT-MS, E-nose) and the acquired data needs to be pre-processed (eg, normalisation, noise filtering, feature extraction). Next, data pre-processing enhances data quality by discarding variance and bias. Feature selection is employed to characterise the variables that have the predictive capacity for the condition of interest. Further, dimensionality reduction techniques mostly need to be utilised to avoid problems related to the curse of dimensionality. Various statistical techniques are employed to detect patterns in the large data sets with either regard to sample classification (supervised) or inconsiderate of the sample classification (unsupervised). After, a predictive model is built on a certain set of samples (training set) and evaluated on another set (validation set) of samples. Model selection is necessary to pick the optimum model with the best performance. Finally, the biological connotation of the obtained results can be given by the usage of metabolic databases such as KEGG database.