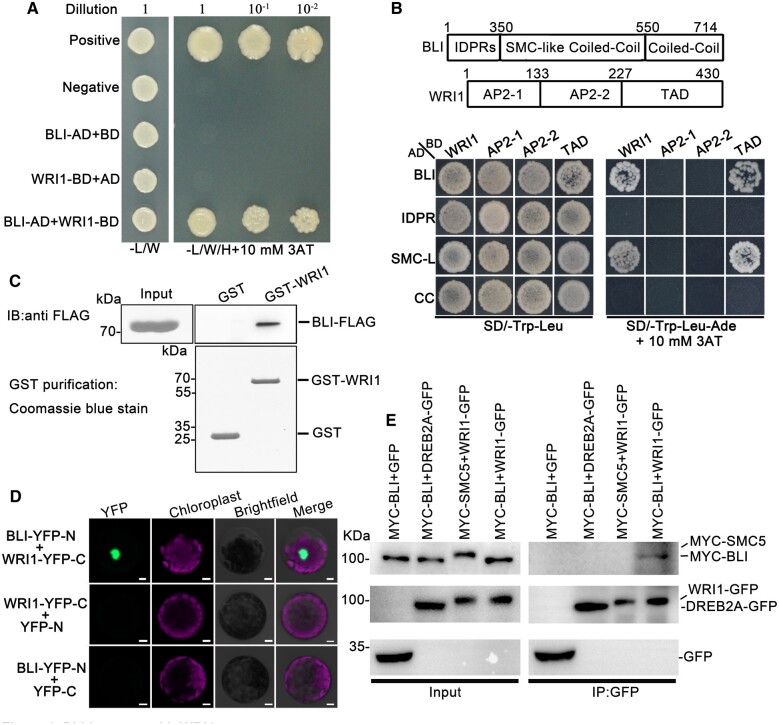
Figure 1.
BLI Interacts with WRI1. A, The interaction between BLI and WRI1 confirmed in YTH assay. Positive control: pGADT7-T + pGBKT7-53; negative control: pGADT7-T + pGBKT7-lam. WRI1-BD, WRI1 fused to GAL4-BD; AD, GAL4-AD vectors without insertion; BLI-AD, BLI fused to GAL4-AD; BD, GAL4-BD vectors without insertion; –L/W, selective medium Trp and Leu. –L/W/H, selective medium lacking Trp, Leu, and Ade. B, Identification of the domains in BLI and WRI1 required for their interaction by YTH analysis. IDPRs, the intrinsically disordered protein regions in BLI. SMC-like CC/SMC-L, the region similar to the CC domain of the chromosomal structural maintenance protein in BLI. CC: the CC domain in BLI. AP2-1/2-2: AP2 domains in WRI1. TAD: Region that contains a transcriptional activation domain in WRI1. C, Interaction between BLI and WRI1 confirmed by in vitro pull-down assay. The BLI-FLAG proteins were incubated with immobilized GST or GST-WRI1, and proteins immunoprecipitated with glutathione Sepharose were detected using anti-FLAG antibody. The amounts of GST and GST-WRI1 are shown in the bottom. D, The interaction between BLI and WRI1 in an in vivo BiFC assay in Arabidopsis protoplasts. Bars = 5 µm. E, The interaction between BLI and WRI1 in an in vivo Co-IP assay. Total protein extracts from transgenic plants carrying both 35S:MYC-BLI and 35S:GFP or both 35S:MYC-BLI and 35S:YFP-WRI1 were immunoprecipitated with the immobilized anti-GFP antibody. The interactions between WRI1 and SMC5 (containing a CC domain), or BLI and the AP2 transcription factor DREB2A were chosen as negative controls. The proteins from crude lysates (left) and IPs (right) were detected using anti-MYC or anti-GFP antibody.