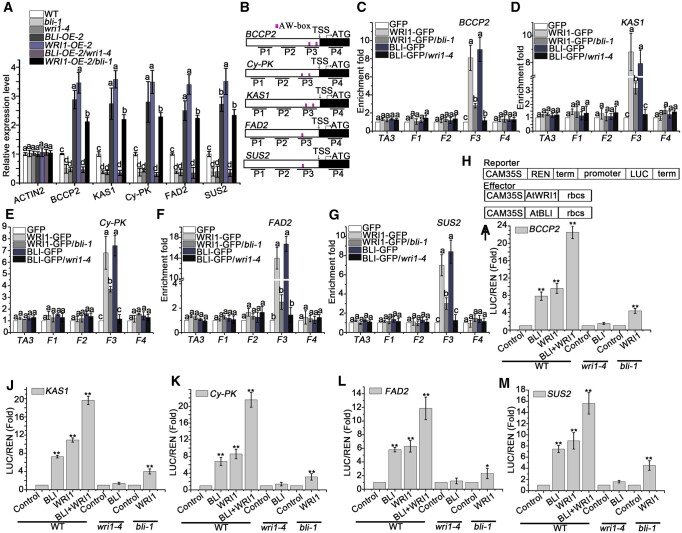
Figure 6.
BLI regulates the expression of WRI1 target genes associated with WRI1 and the transcriptional activity of WRI1. A, RT-qPCR analysis of WRI1 target genes in 12 DAP bli-1, BLI-OE, wri1–4, WRI1-OE, WRI1-OE/bli-1, and BLI-OE/wri1–4 seeds compared to the WT. Data shown are means ± sd (N = 3). UBQ10 was used as a reference gene, and ACTIN2 was used as a negative control. The mean relative expression levels do not significantly differ when they are labeled with the same letter, as determined by Tukey’s HSD test (P < 0.05). B, Schematic diagram of ChIP-qPCR-detected sequences in the WRI1 target genes. White box represents promoters; Magenta vertical line indicates AW-box or AW-box like cis-element sites; Black line indicates ChIP-qPCR-detected sequence; F1–F4 indicate different DNA fragments. C–G, Occupancy of BLI and WRI1 on the promoters of fatty acid biosynthesis genes BCCP2 (C), KAS1 (D), Cy-PK (E), FAD2 (F), and SUS2 (G) in pBLI:BLI-GFP/bli-1 (BLI-GFP), BLI-GFP/wri1–4, pWRI1:WRI1-GFP/wri1-4 (WRI1-GFP), and WRI1-GFP/bli-1 seed compared to GFP control seeds. Data shown are means ± sd (N = 3). The means of enrichment folds do not significantly differ when they are labeled with the same letter, as determined by Tukey’s HSD test (P < 0.05). H, Scheme of the constructs used for dual-LUC assay. The reporter construct consists of the CaMV 35S promoter, five repeats of the GAL4 binding sequence (5xGAL4BS), NOS terminator (NOSter), and firefly LUC coding sequence. Effector constructs express the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (GAL4DB)-fused protein under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter. I–M, Effects of BLI or/and WRI1 on BCCP2 (I), KAS1 (J), Cy-PK (K), FAD2 (L), and SUS2 (M) transcriptional regulation in the WT, bli-1 and wri1–4 Arabidopsis protoplast transient expression assay. Data are means ± sd (n = 3 experiments). Asterisks denote significant difference compared to the control, as determined by Student’s t test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).