Fig. 2.
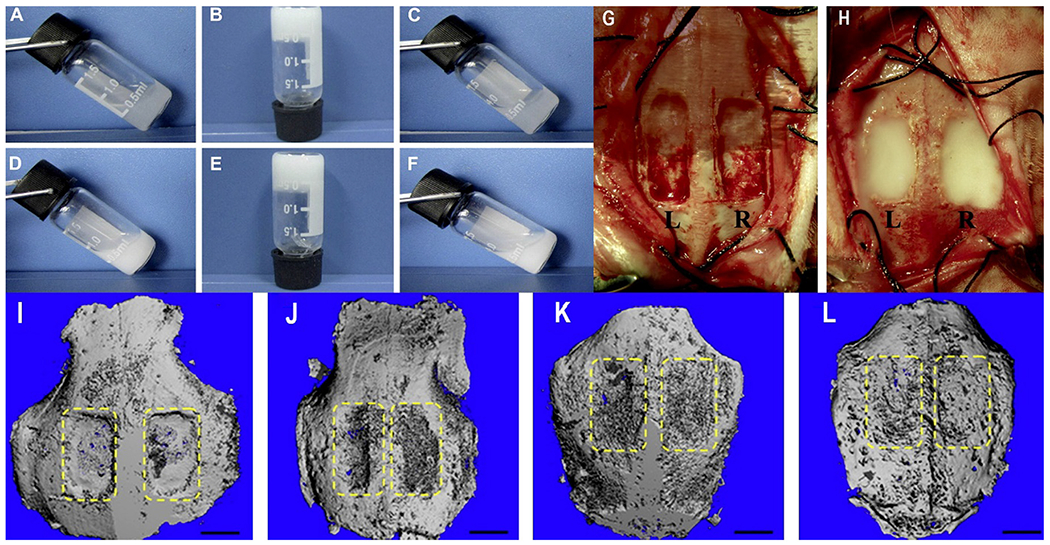
(A-F): Thermosensitivity of ABM/PECE hydrogels at various temperatures. The composites can be seen in sol state at 10 °C (A&D), opaque at physiological temperature 37 °C (B&E) and return to free-flowing sol at 10 °C (C&F). A-C: Pure PECE; D-F: ABM, 30 wt%. G&H: Surgical procedure. G: Filling of the ¼ rectangular cranial defects (12 mm × 8 mm) in New Zealand White rabbits labeled as L left, pure PECE; R ¼ right, ABM/PECE composite. Both the pure PECE (G) and the ABM/PECE composite (H) were gelled in a few minutes at the body temperature. I-L: 3D Micro-computed tomography of cranial defect shows the healing of the cranial defect at various stages of treatment, (I) Surgery moment, (J) 4 weeks, (K) 12 weeks, (L) 20 weeks. [Adopted and modified with permission from Ni et al. [101]].
