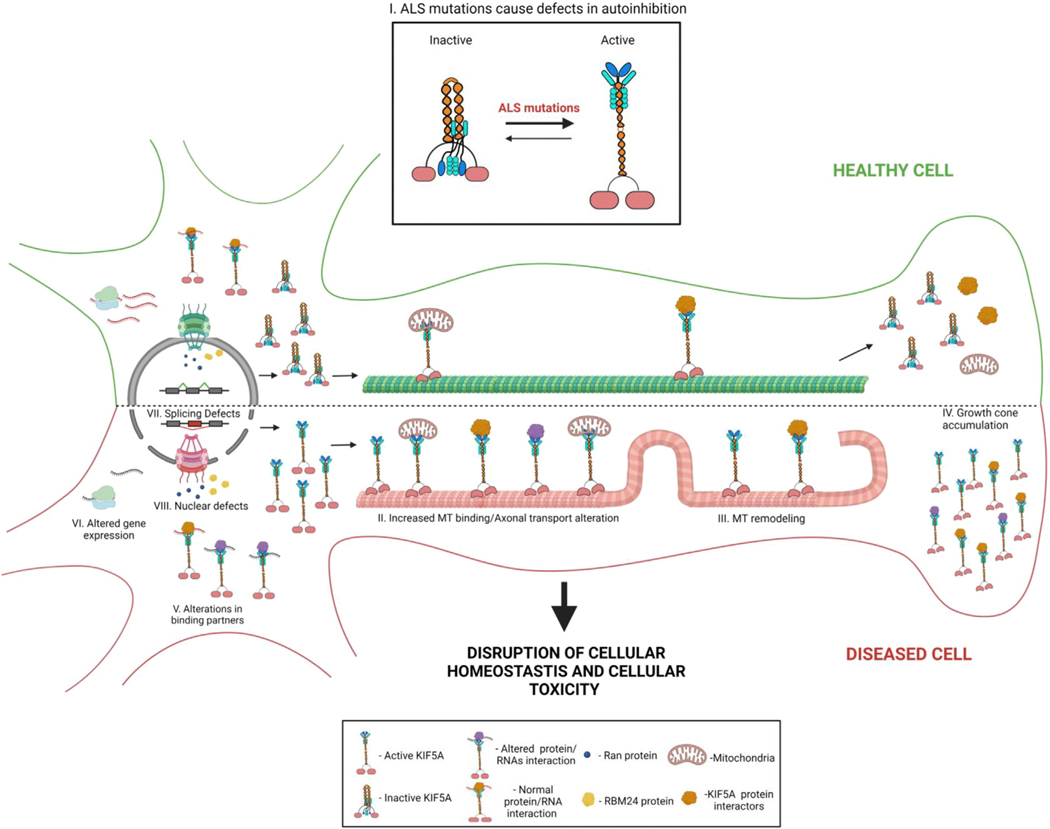
Figure 7. Schematic of how expression of ALS-related mutant KIF5A affects cellular homeostasis leading to cellular toxicity.
ALS-related KIF5A mutations lead to defective autoinhibition (I). As a result, KIF5A has increased binding to MTs and altered axonal transport (II), MT remodeling (III), and growth cone accumulation (IV). The protein and RNA binding partners of mutant KIF5A are also changed (V). On a global scale, differences in gene expression (VI) occur as well as NCT disruptions (VIII) which may affect gene splicing (VII). Ultimately the disruption of cellular homeostasis leads to cellular toxicity and death. This image was created with BioRender.com.