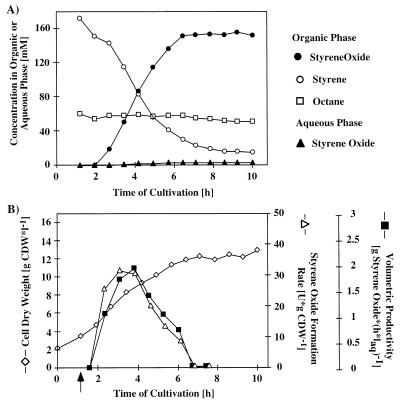
FIG. 5.
Production of (S)-styrene oxide by E. coli JM101(pSPZ3). The culture was grown in a two-liquid-phase medium which contained 25% (vol/vol) hexadecane containing 1% (vol/vol) octane as an inducer and 2% (vol/vol) styrene as the substrate. The organic phase was added 1 h after initiation of feeding. (A) Concentrations of styrene, octane, and styrene oxide in the hexadecane phase and of styrene oxide in the aqueous phase. (B) Formation of E. coli JM101(pSPZ3) biomass and development of productivities. Styrene oxide formation was calculated by determining the total rate of styrene oxide formation per gram (dry weight) of cells (CDW). Volumetric productivity was calculated by determining the mass of styrene oxide formed per hour per liter of aqueous phase (laq).