Figure 5.
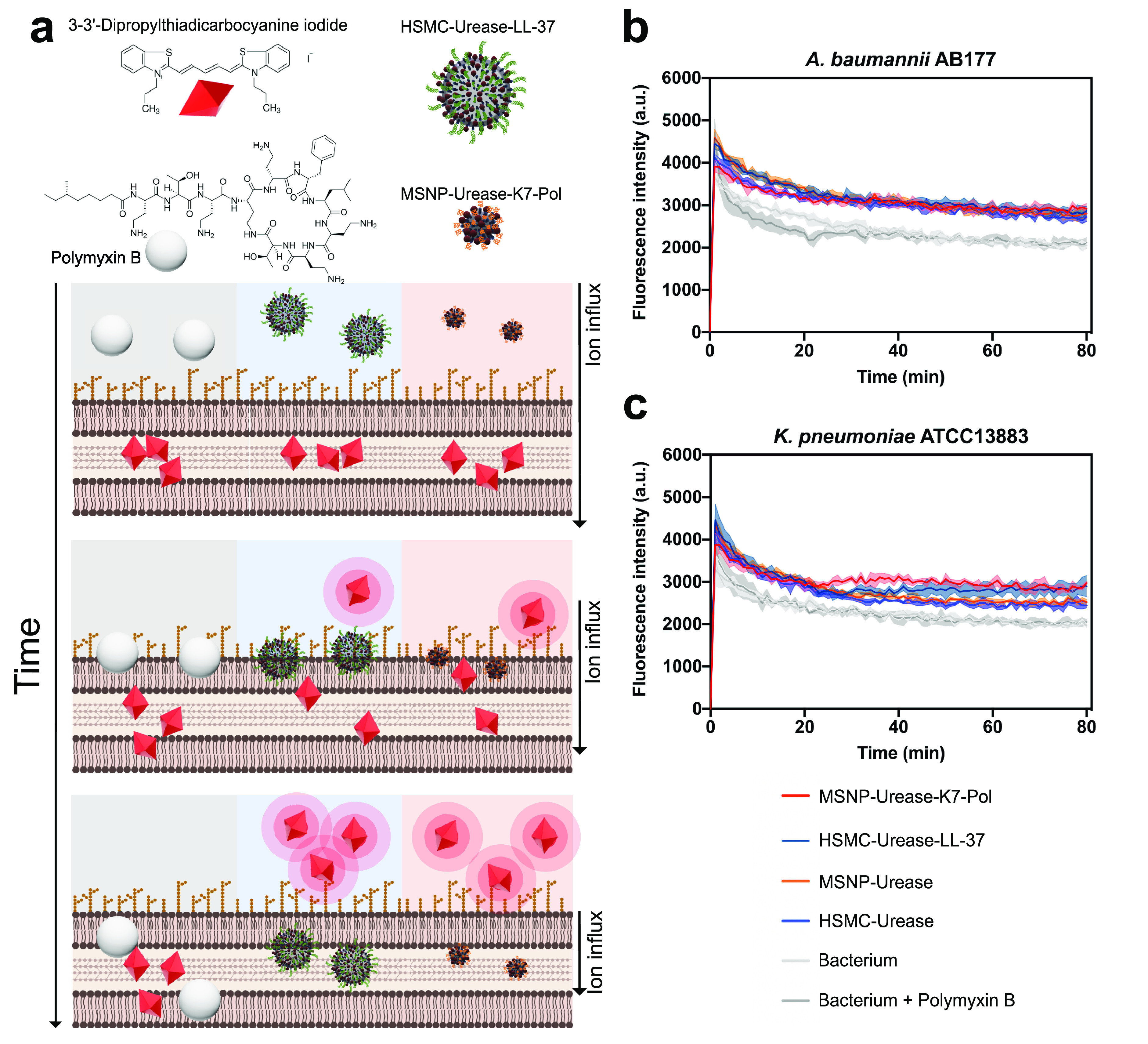
Mechanism of action of the antimicrobial motors. (a) Bioactive micro- and nanomotors cause the depolarization of bacterial membranes at their MIC concentration against (b) A. baumannii AB177 and (c) K. pneumoniae ATCC13883. Briefly, micro- and nanomotors functionalized with LL-37 and K7-Pol, respectively, enabled the higher depolarization of K. pneumoniae cells than the nonfunctionalized motors. When A. baumannii cells were exposed to them both, functionalized and nonfunctionalized motors presented depolarizing effect. The potent permeabilizer antimicrobial polymyxin B was used as a negative control for depolarization. Assays were performed in three independent replicates. This figure was created with BioRender.com.
