FIGURE 6.
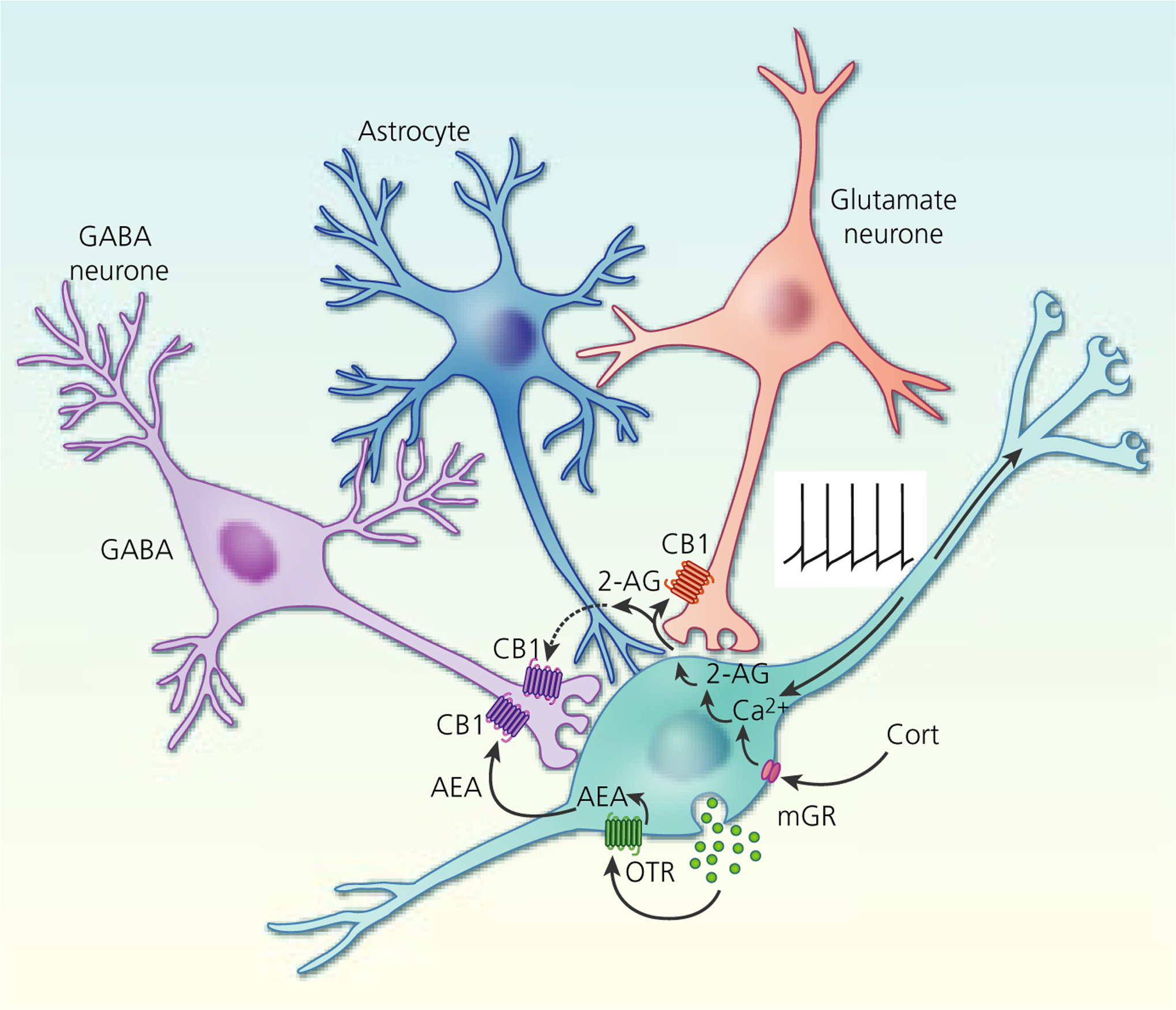
Endocannabinoid modulation of excitatory and inhibitory synapses on magnocellular neurosecretory cells (MNCs). Oxytocin activation of autocrine oxytocin receptors (OTR) on oxytocin neurones leads to a tonic basal release of the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA) at GABA synapses, which tonically suppresses synaptic inhibitory input to oxytocin neurones by activating presynaptic CB1 receptors. Depolarisation (eg, via action potential generation) or corticosteroid (Cort) activation of membrane glucocorticoid receptors (mGR) (eg, during stress) leads to a calcium-dependent release of the other main endocannabinoid, 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), at glutamate synapses, which suppresses synaptic excitation of both oxytocin and vasopressin MNCs by activating presynaptic CB1 receptors. Glial retraction induced by salt loading allows the 2-AG released at glutamate synapses to spill over onto GABA synapses and suppress synaptic inhibition via CB1 receptor activation. Tonic AEA occupation of CB1 receptors at GABA synapses is non-saturating, allowing additional suppression of GABA release following phasic 2-AG release and synaptic spillover
