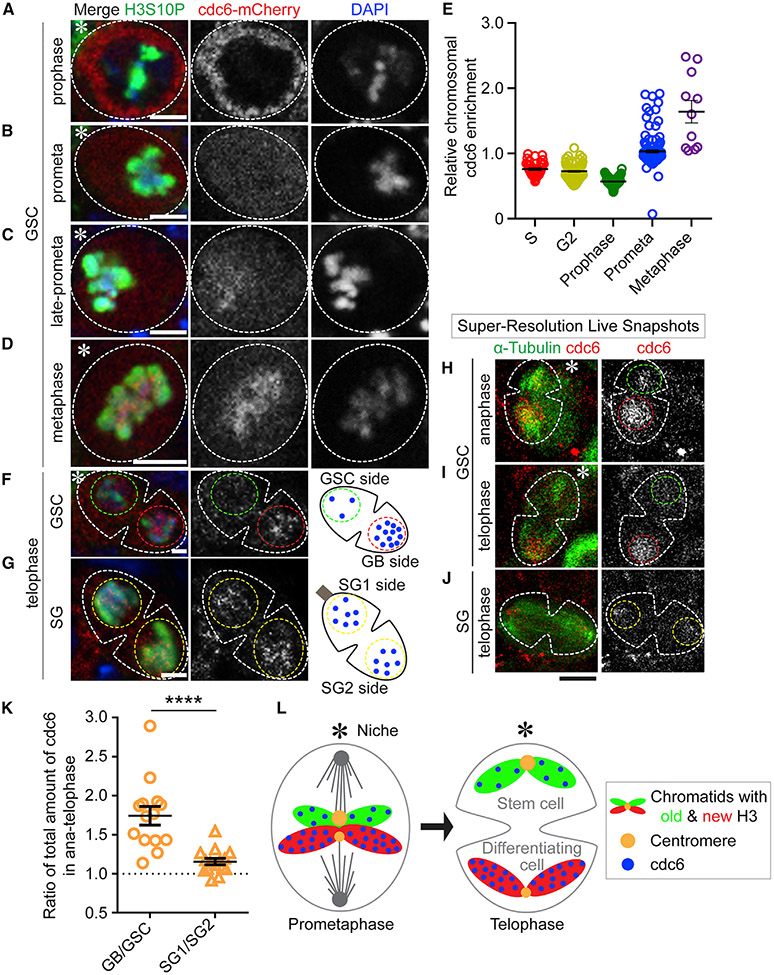
Figure 3. Cdc6 binds to chromatin during mitosis and segregates asymmetrically to the GB during ACD of GSCs.
(A–D) In GSCs, Cdc6 localizes in the cytoplasm during prophase (A), gradually associates with the mitotic chromatin during prometaphase (B and C), and strongly associates with chromatin at metaphase (D).
(E) Quantification of the Cdc6 association with chromatin (see Figure S3A, S phase: 0.76 ± 0.02 [n = 36]; G2 phase: 0.73 ± 0.01 [n = 98]; prophase: 0.57 ± 0.01 [n = 70]; prometaphase: 1.03 ± 0.02 [n = 120]; metaphase: 1.64 ± 0.17 [n = 11]).
(F and G) Segregation of Cdc6 during mitosis in GSCs (F) and SGs (G) by fixed cell imaging.
(H–J) Airyscan SRLS for Cdc6 segregation pattern in an anaphase GSC (H), a telophase GSC (I), and a telophase SG (J).
(K) Distribution of Cdc6 in anaphase/telophase GSCs and SGs (GB/GSC: 1.74 ± 0.12 [n = 14]; SG1/SG2: 1.16 ± 0.04 [n = 15]), ****p < 10−4 by Mann-Whitney t test, Table S8, see Mendeley data.
(L) A model for the differential binding of Cdc6 to new H3-enriched sister chromatids followed by asymmetric segregation to the GB. Scale bars, 2 μm in (A–D, F–G) and 5 μm in (H–J). Asterisk: hub. All ratios = average ± SE.