FIG. 1.
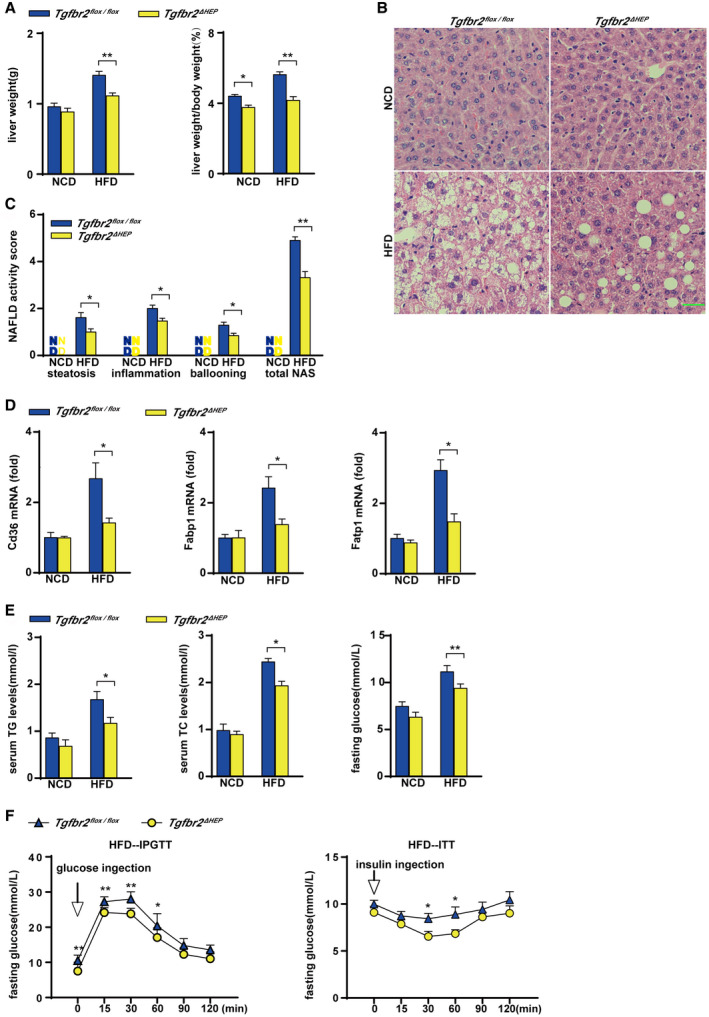
Hepatocyte‐specific deletion of Tgfbr2 mitigates steatosis and insulin resistance induced by HFD consumption. Tgfbr2flox/flox and Tgfbr2ΔHEP mice were fed an NCD or an HFD for 16 weeks; n = 7 per group. (A) Liver weight and ratio of liver weight to body weight in HFD‐fed mice. (B) Representative images of H&E‐stained liver section after HFD feeding as indicated (×400; green bar represents 10 μm). (C) NAFLD activity score after HFD fed as indicated, scoring by two observers in a blinded fashion. (D) Hepatic mRNA expression of genes related to fatty acid transport in HFD‐fed mice. (E) Serum TG and TC levels and fasting glucose levels in HFD‐fed mice. (F) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test and insulin tolerance test of HFD‐fed Tgfbr2flox/flox and Tgfbr2ΔHEP mice. Two‐way ANOVA was used for all statistical analysis. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). Tgfbr2ΔHEP ‐NCD versus Tgfbr2flox/flox ‐NCD, and Tgfbr2ΔHEP ‐HFD versus Tgfbr2flox/flox ‐HFD were examined. Abbreviations: IPGTT, intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test; ITT, insulin tolerance test.
