FIG. 6.
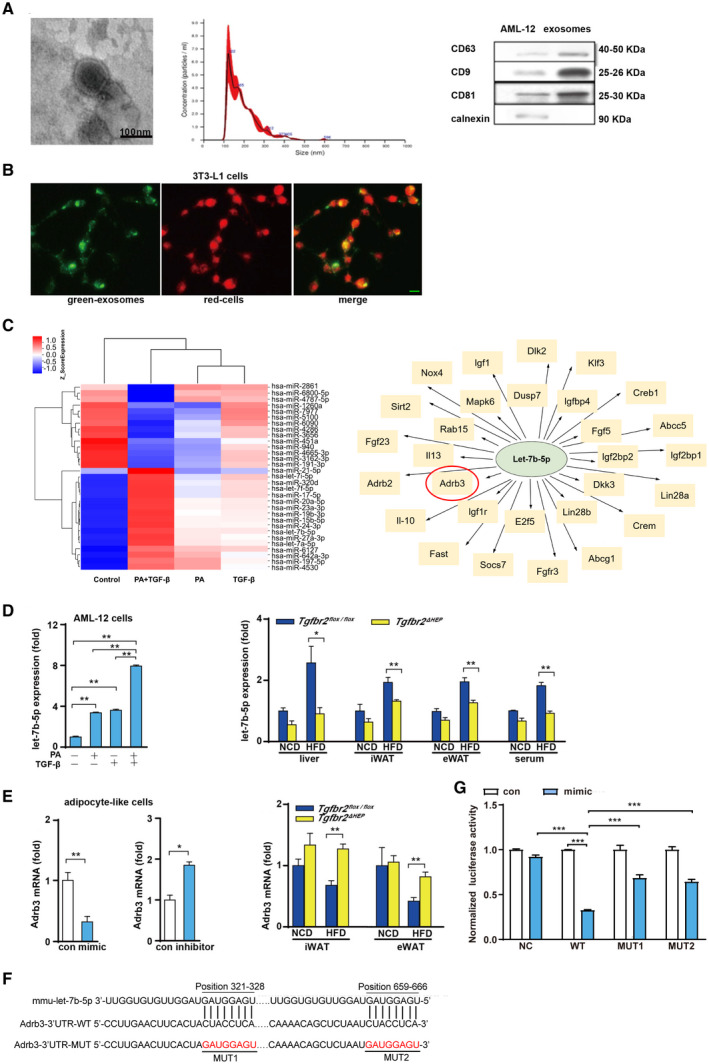
PA and TGF‐β cooperatively induce the production of exosomes containing let‐7b‐5p by hepatocytes. (A) Left: Electron microscopy analysis of exosomes released by AML‐12 cells (scale bar represents 100 nm); middle: size distribution profile of exosomes as determined by NTA; right: western blot analysis of CD9, CD63, CD81, and calnexin in AML‐12 cells and exosomes. (B) Exosomes internalized by 3T3‐L1 cells (green denotes exosomes and red indicates cells; green bar indicates 5 μm). (C) Heat map showing some significantly differentially expressed miRNAs in exosomes from LO2 cells treated with PA plus TGF‐β compared with control exosomes, and some predicted target genes of hsa‐let‐7b‐5p. (D) Let‐7b‐5p levels in exosomes derived from AML‐12 cells after challenged with PA and TGF‐β for 24 hours, and let‐7b‐5p expression in the liver, iWAT, eWAT, and serum exosomes in a mouse model of obesity. (E) Adrb3 levels in MEF‐like adipocyte cells after let‐7b‐5p mimic and inhibitor exposure and in iWAT and eWAT of Tgfbr2flox/flox and Tgfbr2ΔHEP mice. (F) Binding sites between let‐7b‐5p and Adrb3 mRNA 3′UTR in WT and MUT plasmids. (G) Luciferase activity after 293T cells co‐transfected with dual‐luciferase reporter vector along with let‐7b‐5p mimics or mimics NC. One‐way ANOVA and Two‐way ANOVA were used for statistical analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). The in vivo experiment examined Tgfbr2ΔHEP ‐NCD versus Tgfbr2flox/flox ‐NCD and Tgfbr2ΔHEP ‐HFD versus Tgfbr2flox/flox ‐HFD; the in vitro experiment, in which PA+TGF‐β represents the group treated with PA and TGF‐β, examined the control versus TGF‐β and the control versus PA+TGF‐β, and PA/TGF‐β versus PA+TGF‐β. Abbreviations: MUT, mutant; NC, negative control. Dlk2, delta like non‐canonical Notch ligand 2; Klf3, Kruppel like factor 3; Creb1, cAMP responsive element binding protein 1; Abcc5, ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 5; Igf2bp1, insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1; Lin28a, lin‐28 homolog A; Crem, cAMP responsive element modulator; Abcg1, ATP binding cassette subfamily G member 1; Fgfr3, fibroblast growth factor receptor 3; Socs7, suppressor of cytokine signaling 7; Fast, Fas activated serine/threonine kinase; Il‐10, interleukin 10; Adrb2, adrenergic receptor, beta 2; Fgf23, fibroblast growth factor 23; Sirt2, sirtuin 2; Nox4, NADPH oxidase 4; Igf1, insulin‐like growth factor 1; Dusp7, dual specificity phosphatase 7; Igfbp4, insulin‐like growth factor binding protein 4; Fgf5, fibroblast growth factor 5; Igf2bp2, insulin‐like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2; Dkk3, dickkopf WNT signaling pathway inhibitor 3; Lin28b, lin‐28 homolog B; E2f5, E2F transcription factor 5; Igf1r, insulin‐like growth factor 1 receptor; Il13, interleukin 13; Rab15, RAB15, member RAS oncogene family; Mapk6, mitogen‐activated protein kinase 6.
