Figure 3: HPK-1 promotes proteostasis.
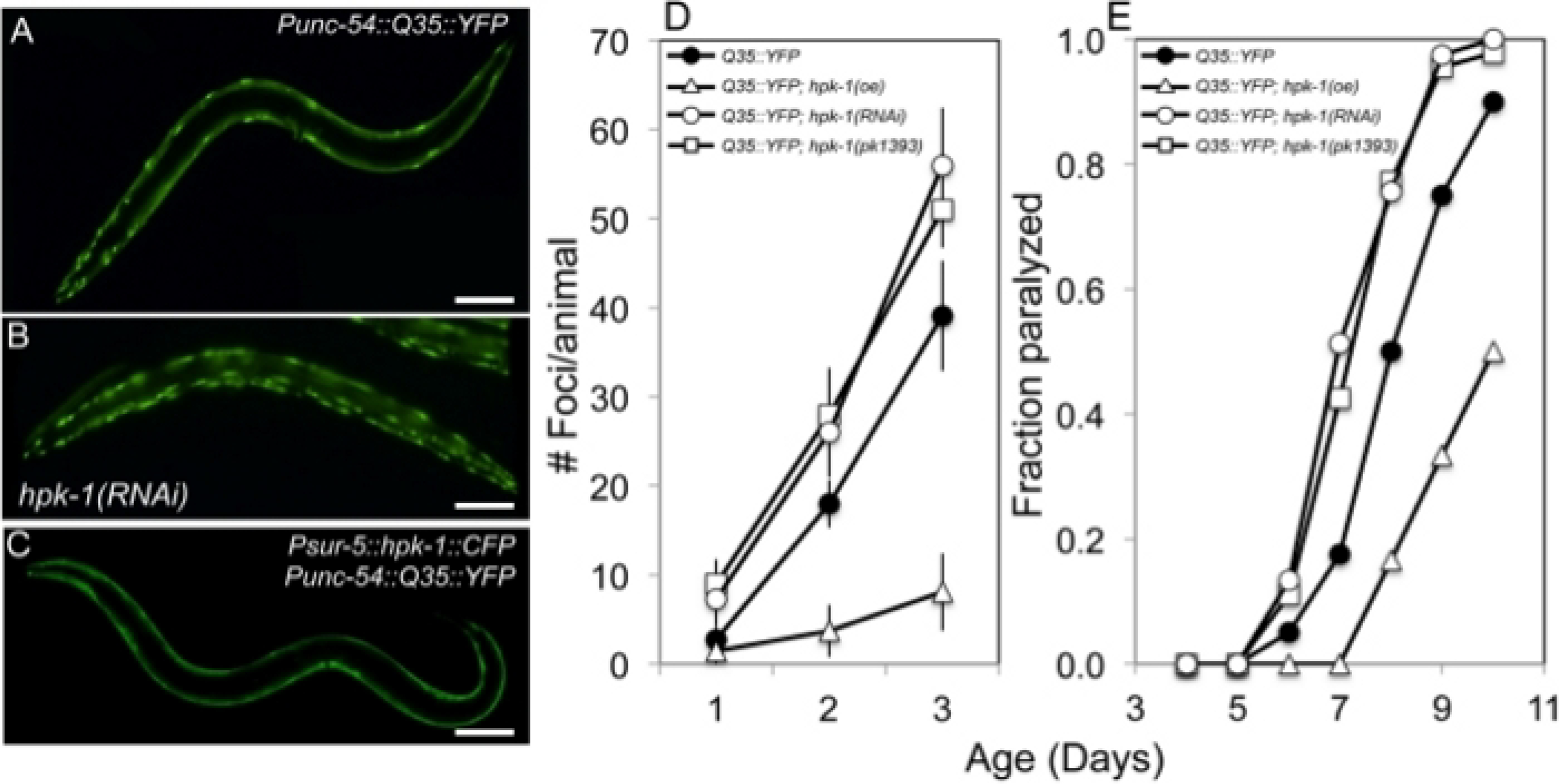
(A-C) hpk-1 activity affects the accumulation of Q35::YFP foci in muscle cells. Shown are representative images of Punc-54::polyQ::YFP animals treated with (A) control RNAi or (B) hpk-1 RNAi, and (C) transgenic animals overexpressing hpk-1 (Psur-5::HPK-1::CFP). (D) Time course of polyQ::YFP foci accumulation in conjunction with: treatment with control RNAi (black circles), hpk-1 RNAi (white circles), hpk-1(pk1393) (white squares), or hpk-1 overexpression (open triangles). Data points display the mean ± standard deviation (S.D.) of at least 15 animals per biological replicate; at least 5 independent experiments were performed. (E) Time course of paralysis of Punc-54::polyQ::YFP animals in conjunction with: treatment with control RNAi (black circles), hpk-1 RNAi (white circles), hpk-1(pk1393) (white squares), or hpk-1 overexpression (open triangles). Plotted data display the results for a single representative trial. This figure is reprinted from reference31 with permission via a Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. The scale bar represents 100 μm in all panels.
