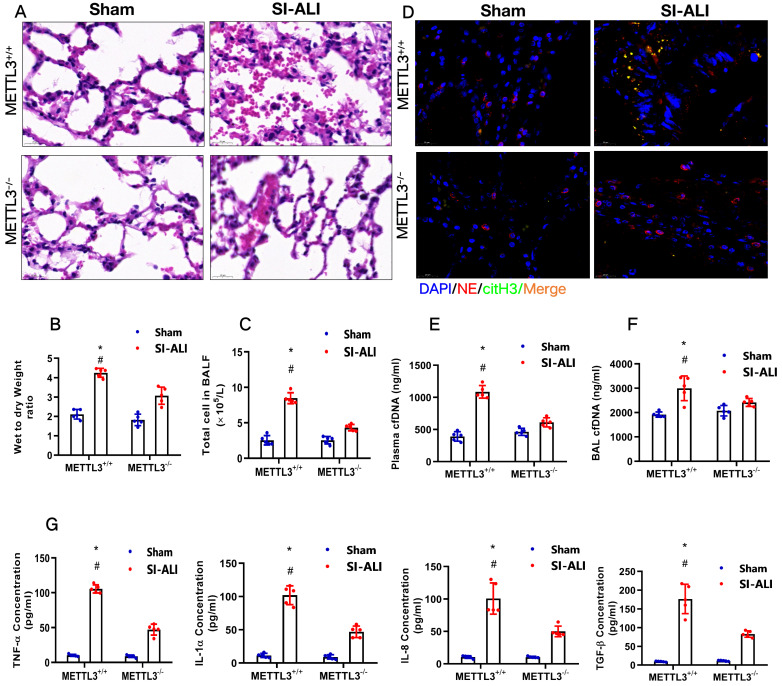
Figure 9.
METTL3 knockout protects mice against sepsis-associated ALI. (A) Paraffin-embedded mouse lung tissue samples were stained with H&E. Representative histological images were shown at 400× magnification. Scale bar=50 µm. (B) Pulmonary edema was evaluated by determining the wet/dry weight ratio in a mouse model (n=6). (C) The cells in extracted BALF were analyzed by cell counting in a mouse model (n=6). (D) Representative images of immunofluorescence staining of NETs in lung tissues from METTL3+/+ and METTL3-/- murine models in the sham and sepsis-associated lung injury group (red: NE, green: CitH3, blue: DAPI). (E) The cfDNA level in plasma (n=6) and (F) BALF was detected in METTL3+/+ and METTL3-/- murine models in the sham and sepsis-associated lung injury groups (n=6). (G) The level of TNFα, IL-1α, IL-8 and TGF-β were determined by ELISA in METTL3+/+ and METTL3-/- murine models in the sham and sepsis-associated lung injury groups (n=6). *P<0.05 (Two-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction).