Fig. 1.
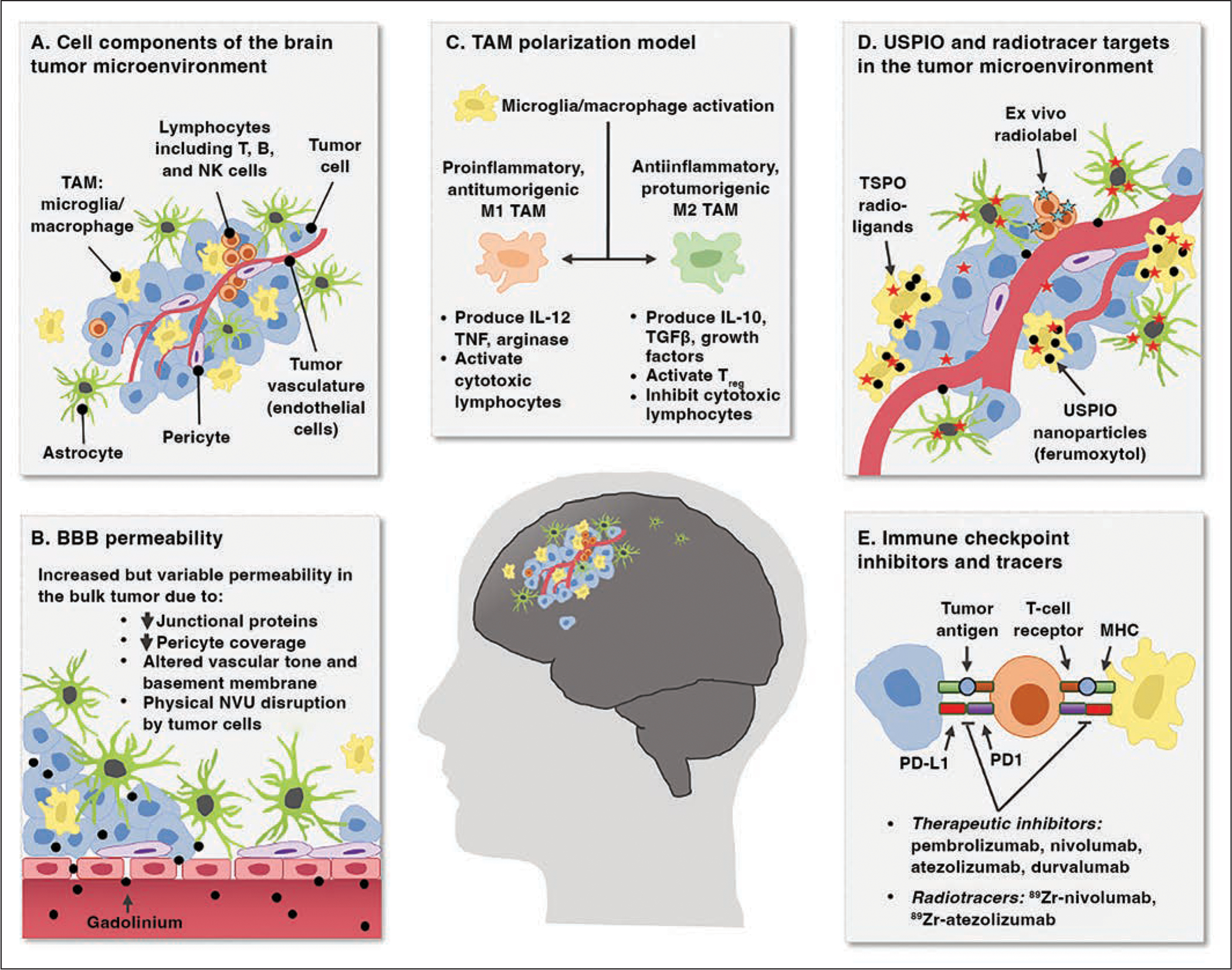
Chart shows neuroinflammation in brain tumor microenvironment presenting noninvasive imaging targets.
A, Cellular components of brain tumor microenvironment include milieu of resident and infiltrating cells, including neoplastic primary or metastatic tumor cells, lymphocytes, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), astrocytes, pericytes, and endothelial cells. NK = natural killer.
B, Blood-brain barrier (BBB) has variable permeability in brain tumors that is clinically visualized as intraparenchymal leakage of gadolinium contrast agent. NVU = neurovascular unit, ↓ = decreased.
C, TAMs in brain tumors can be differentially activated into proinflammatory and antiinflammatory reactive states that have opposing effects on tumor control and further propagate neuroinflammation through production and secretion of soluble immune-modulating factors. IL = interleukin, Treg = regulatory T cells, TGFβ = transforming growth factor β, TNF = tumor necrosis factor.
D, Intravascularly delivered contrast agents and radioligands have potential for selective labeling of key immune elements of brain tumor microenvironment for noninvasive tracking. Specific expression and uptake distribution of these molecules is area of active investigation that is debated. USPIO = ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide, TSPO = translator protein.
E, Immune checkpoints in brain tumor microenvironment are expressed by several cell types. Recent evidence suggests possible contribution of innate immune cell types. These checkpoints are target of multiple immunotherapies, and development of radiotracers to track their expression is underway. MHC = major histocompatibility complex, PD1 = programmed cell death 1, PD-L1 = programmed cell death ligand 1.
