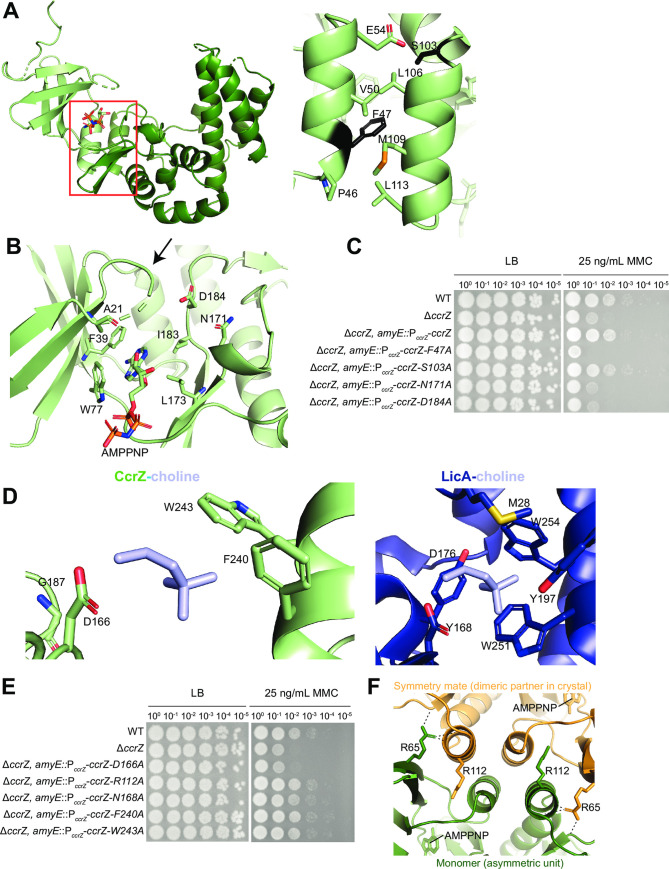
Fig 4. Functional assessment of CcrZ structural features.
(A) Interaction between two alpha-helices from the N and C terminal lobes of CcrZ. Position in overall structure (left) and residues within the helices (right). F47 and S103 are shown in black. (B) CcrZ P-loop (arrow) and catalytic residues highlighted. (C) Alanine substitutions of residues in the alpha-helix and catalytic site abolish activity in vivo. (D) Hydrophobic binding pocket in LicA-choline (right) and CcrZ with choline overlaid (left). Hydrophobic caging residues in LicA and corresponding residues in CcrZ are annotated. (E) Alanine substitutions of residues within the binding pocket of CcrZ do not abolish activity in vivo. (F) Cartoon representation of the dimeric interface in the crystal with AMP-PNP; R112 and R65 on each monomer shown in sticks. H-bonds formed by the side chain of R65 of one monomer with the protein backbone of the other monomer in the crystal are shown as dashed lines.