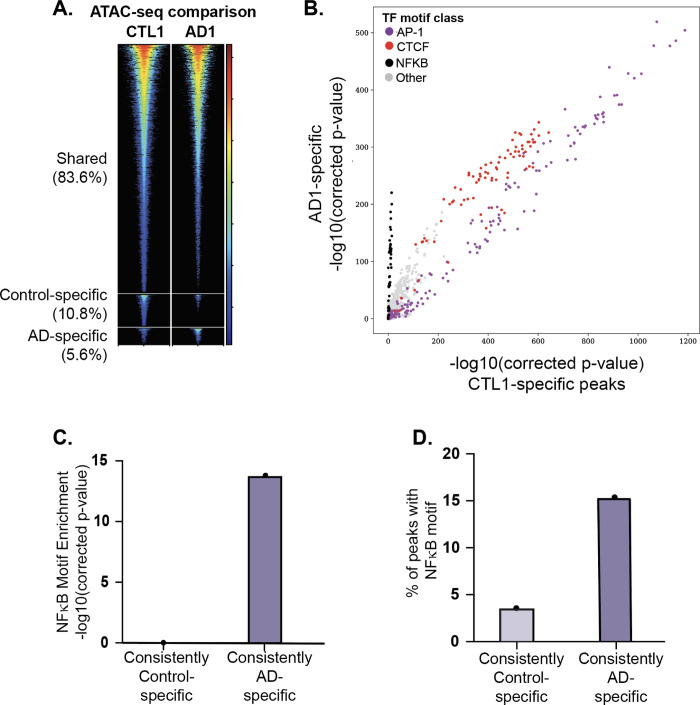
Fig 2. Differential chromatin accessibility and transcription factor (TF) motif enrichment in atopic dermatitis (AD) subjects vs. matched controls.
Assay for transposase-accessible chromatin sequencing (ATAC-seq) peaks were identified for all cases and controls and compared for all subject pairs. (A) Differential chromatin accessibility analysis. For each matched pair of subjects, we identified shared, control-specific, and AD-specific peaks (see METHODS). A representative subject pair is shown in (A). Each row represents a single genomic locus where an ATAC-seq peak was identified in either the AD or control subject. The center of each row corresponds to the center of the ATAC-seq peak. Heatmap colors indicate the normalized ATAC-seq read count within the AD1 (right) or CTL1 (control) (left) subject–see key on the right. (B) Differential transcriptional factor (TF) motif enrichment analysis. Comparison of TF motif enrichment results within a representative AD-specific and control-specific matched subject pair. Each dot represents the enrichment of a particular motif (corrected negative log10 p-value). Select motif families are color-coded (see key on the upper left side). (C and D) Nuclear factor kappa B (NFKB) motif enrichment comparison between consistently AD-specific and consistently control-specific ATAC-seq peaks. “Consistently specific” peaks were defined as those peaks that were AD- or control-specific in at least three AD or control subjects, respectively. Results are shown for representative Cis-BP NFKB motif, M05887_2.00. Full results are provided in S5 Table.