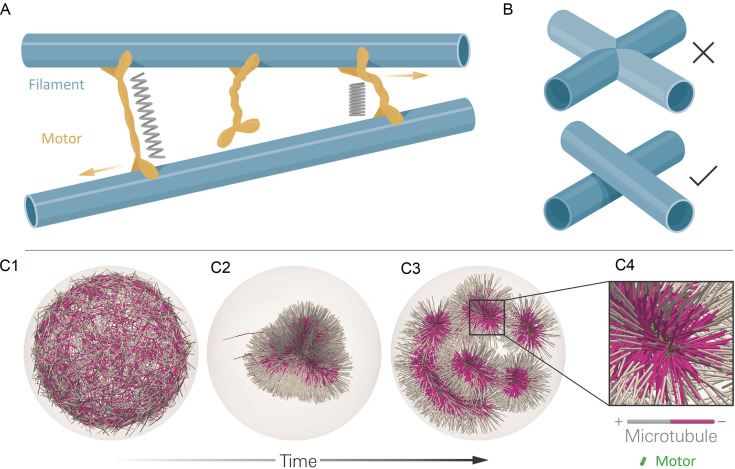
Figure 1. The computational model and demonstration of aLENS.
(A) aLENS simulates dynamics of rigid filaments crosslinked and driven by motors, thermal fluctuations, and steric interactions. Motors bind to, unbind from, and walk along filaments. (B) To achieve high efficiency, aLENS computes motor forces implicitly, and steric interactions through a novel geometric constraint method that avoids filament overlaps. (C1-C3) Example simulation of microtubules organized into asters by minus-end-directed motors. The 300 s Brownian simulation contains 3200 microtubules, each 1 µm long, inside a sphere of radius 3 µm. The initial position of each microtubule is random and the half of each filament on the minus-end is colored pink. Three end-pausing dynein motors are fixed at the minus-end of each microtubule and walk toward the minus-end of any microtubule they crosslink. After initial contraction into a single large aster, strong steric interactions in the aster center break up the system into several smaller asters and a bottle-brush structure. (C4) Motors are highly concentrated at the centers of asters.