Figure 16.
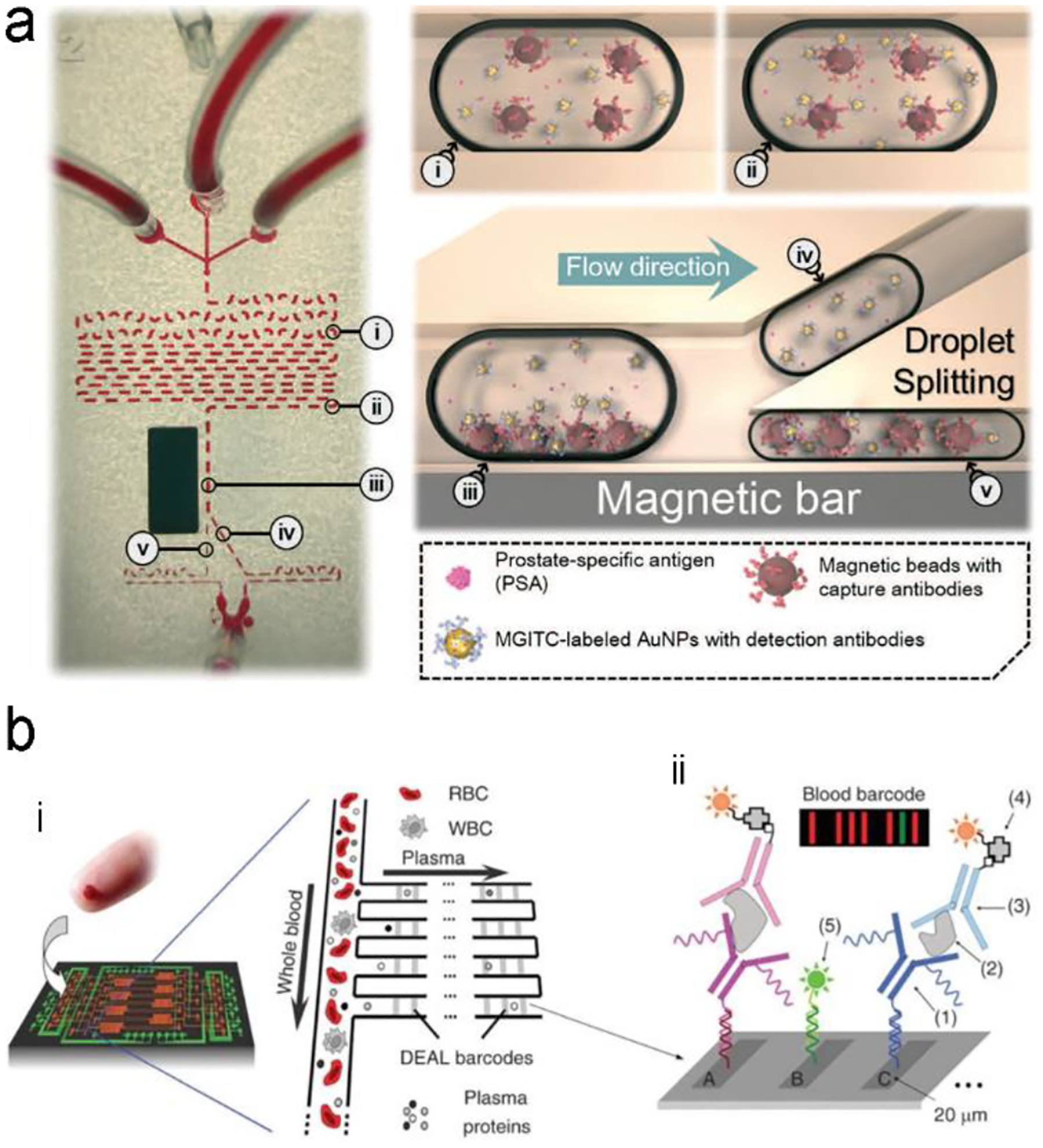
A typical structure of active optofluidic device for protein detection. (a) SERS-based microdroplet device for detection of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) cancer markers. It has 5 compartments with different functions: (i) generating microdroplet and mixing reagents; (ii) forming immunocomplexes on magnetic beads; (iii) separating immunocomplexes by magnetic bar; (iv) moving the supernatant that contained the unbound SERS probes; and (v) separating magnetic immunocomplexes through droplet splitting. (b) In vitro fluorescence microfluidic device for multiplexed detection of proteins in finger-prick whole blood. Reproduced with permission from (a) ref. 218, copyright 2016, The Royal Society of Chemistry; (b) ref. 235, copyright 2008, Springer Nature.
