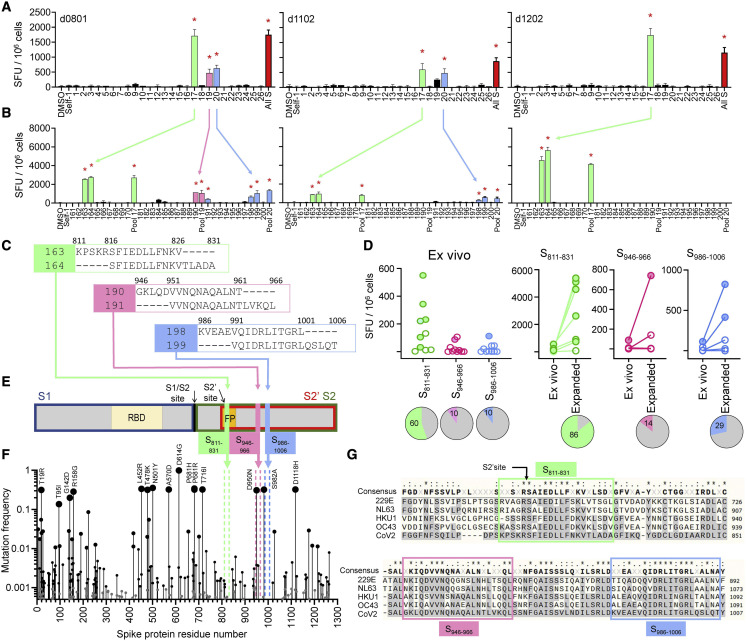
Figure 2.
Identification of cross-reactive peptides
(A) IFN-γ ELISpot responses of in vitro HCoV-expanded lines from 3 COVID-19 donors to re-stimulation with SARS-CoV-2 S overlapping peptide pools (pool number on x axis; all S, all S peptides; DMSO and Self-1, negative controls).
(B) Deconvolution of positive pools (peptide number on x axis; parent pool included).
(C) Amino acid sequences of candidate epitopes: S811–826/S816–831 (green), S946–961/S951–966 (pink), and S986–1,001/S991–1,006 (blue).
(D) Ex vivo responses to candidate epitopes in 10 COVID-19 donors, comparison of ex vivo and in vitro expanded responses (filled circles, positive; empty circles, negative by DFR2X). Pies: percentage of positive responses.
(E) Schematic of SARS-CoV-2 S protein with location of candidate epitopes. RBD, receptor binding domain; FP, fusion peptide; cleavage sites (S1/S2 and S2′) and cleavage products S1 (blue box), S2 (green box), and S2ʹ (red box).
(F) Mutation frequency is indicated by size of circles. Location of candidate epitopes in the protein shown by colored broken vertical lines. Common mutations are also indicated.
(G) Sequence alignment of S proteins from SARS-CoV-2 (bottom) and HCoVs (229E, NL63, HKU1, and OC43) in the region of the candidate epitopes (enclosed in boxes).
For (A) and (B), bar graphs: means ± standard deviations; red stars: positive responses by DFR2X.