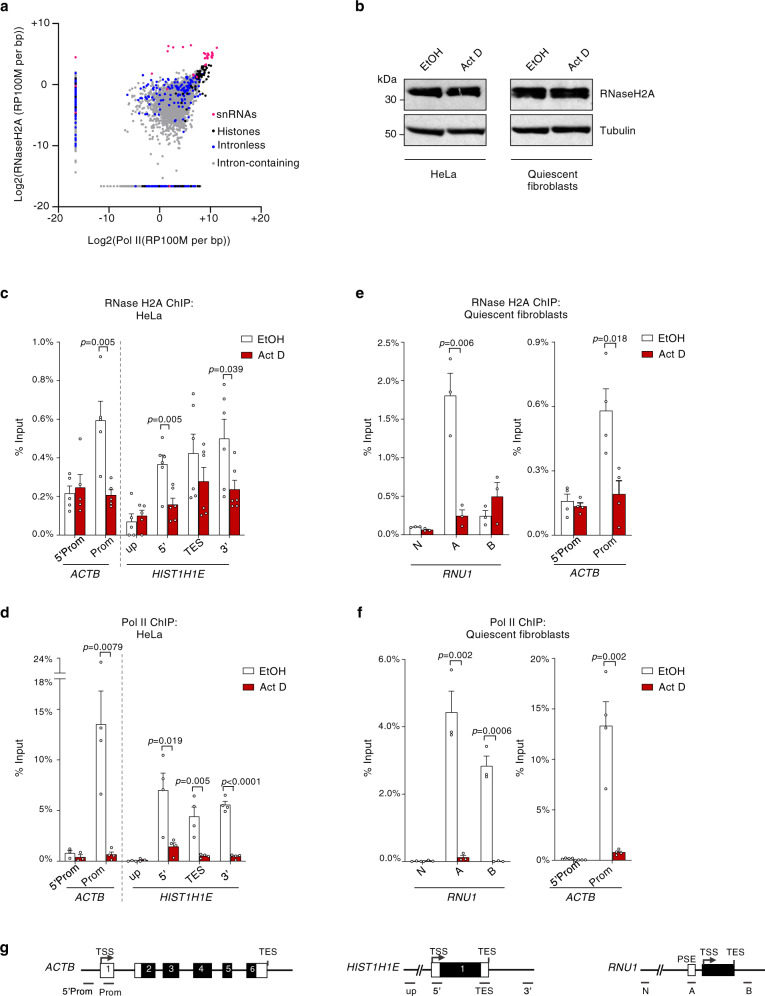
Fig. 2. RNase H2A binding is transcription-dependent.
a Scatterplot of RNase H2A versus Pol II ChIP signal across genes, defined as TSS to TES. Genes with RNase H2A or Pol II ChIP signal positive over the input are shown. snRNA (pink), histone (black), intronless (blue) and intron-containing (gray) genes are shown. b Western blot of RNase H2A in HeLa cells and quiescent fibroblasts treated with actinomycin D (Act D) and ethanol (vehicle). Tubulin is a loading control. Representative blots from n = 2 biologically independent experiments. c RNase H2A ChIP-qPCR and d Pol II ChIP-qPCR of ACTB and HIST1H1E genes in HeLa cells, treated with ethanol (vehicle; white bars) or actinomycin D (Act D; red bars). Values represent percentage of input (means ± SEM). p-values were calculated using two-tailed unpaired t-test. n = 5 or 6 biologically independent experiments in c. n = 3 or 4 biologically independent experiments in d. e RNase H2A ChIP-qPCR and f Pol II ChIP-qPCR of RNU1 and ACTB genes in WI38 hTERT cells (quiescent fibroblasts), treated with ethanol (vehicle; white bars) or actinomycin D (Act D; red bars). Values represent percentage of input (means ± SEM). p-values were calculated using two-tailed unpaired t-test. n = 3 (RNU1) or n = 4 (ACTB) biologically independent experiments. g Diagrams of the indicated genes. Source data are provided as a Source data file.