Fig. 7. Transgenic mosquitoes strongly inhibit P. berghei transmission to mice.
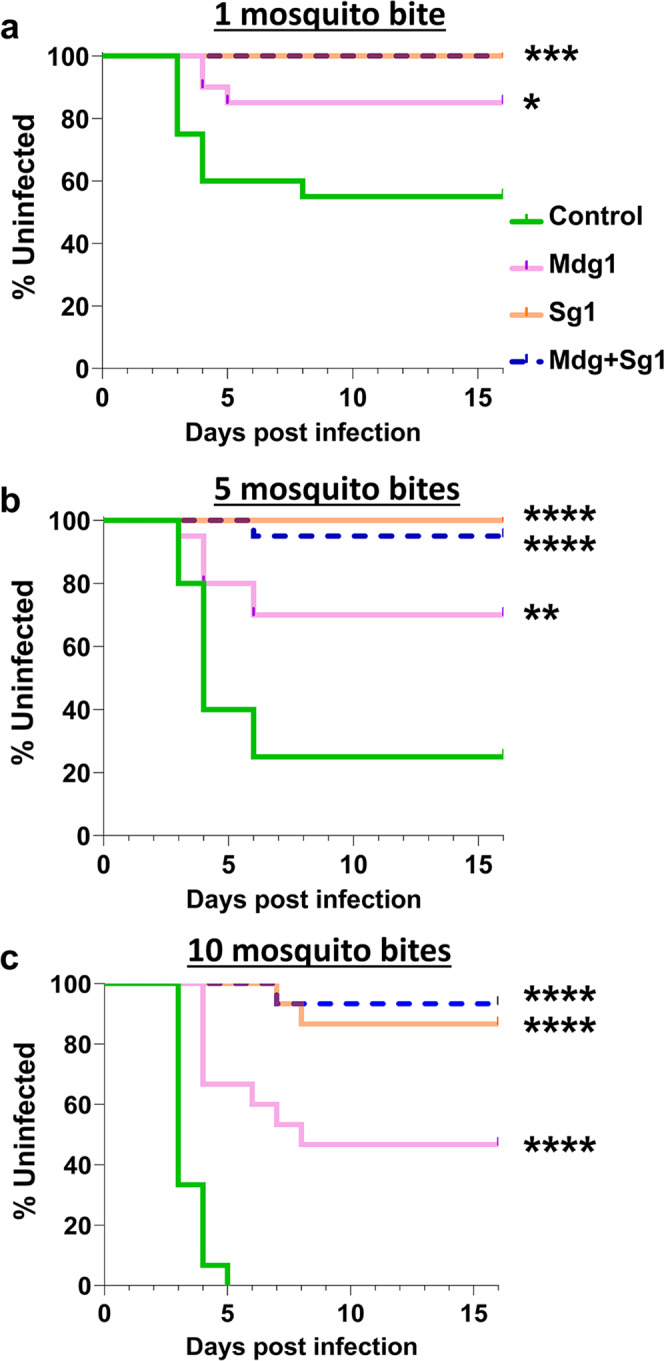
a–c WT and transgenic mosquitoes were fed on the same P. berghei infected mouse, and unfed mosquitoes were removed. To determine their potential to transmit malaria, mosquitoes were randomly selected at 21 days post-infection and fed on naïve mice (challenge). Each mouse was challenged with one (a), five (b), or ten (c) mosquitoes. Infection was determined by daily monitoring blood-stage parasites on Giemsa-stained blood smears. Statistical analysis was determined by Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test with α = 0.05 and k = 0.0166. Data from 1 and 5 mosquitoes, N = 10 mice per group per replicate, with two replicates (total 20 mice). Data from 10 mosquitoes, N = 15 mice, 10 mice per group for one replicate and 5 mice per group for the second replicate (total 15 mice). a: *P = 0.0306, ***P = 0.0007. b: **P = 0.0036, ****P < 0.0001. c: ****P < 0.0001. The oocyst number for the mosquitoes used for the challenge is shown in Supplementary Data 1, Dataset 8.
