Figure 5.
APN is a functional entry receptor for CCoV-HuPn-2018
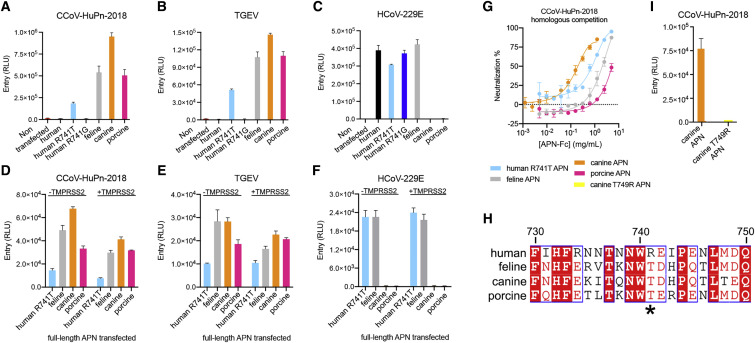
(A–C) Entry of VSV particles pseudotyped with CCoV-HuPn-2018 S (A), TGEV S (B), or HCoV-229E S (C) in HEK293T cells transiently transfected with human, human R741T (glycan knockin), human R741G, feline, canine, or porcine APN orthologs. RLUs, relative luciferase units.
(D–F) Entry of VSV particles pseudotyped with CCoV-HuPn-2018 S (D), TGEV S (E), and HCoV-V229E S (F) in HEK293T cells transiently transfected with human R741T (glycan knockin), canine, feline, or porcine APN orthologs in the presence or absence of TMPRSS2.
(G) Concentration-dependent inhibition of CCoV-HuPn-2018 S pseudovirus entry in HEK293T cells transiently transfected with full-length APN orthologs with matched, purified dimeric soluble APN-Fc ectodomains.
(H) Sequence alignment of human, feline, canine, and porcine APNs focused on the N739 glycosylation sequon. Human APN position 741 is indicated with an asterisk. Residue numbering corresponds to human APN.
(I) Entry of VSV particles pseudotyped with CCoV-HuPn-2018 S in HEK293T cells transiently transfected with canine or canine T749R glycan knockout mutant (equivalent to human APN position 741).
Mean and standard deviation of technical duplicates are graphed. See also Figures S3, S5, and S6 and Tables S3 and S4.