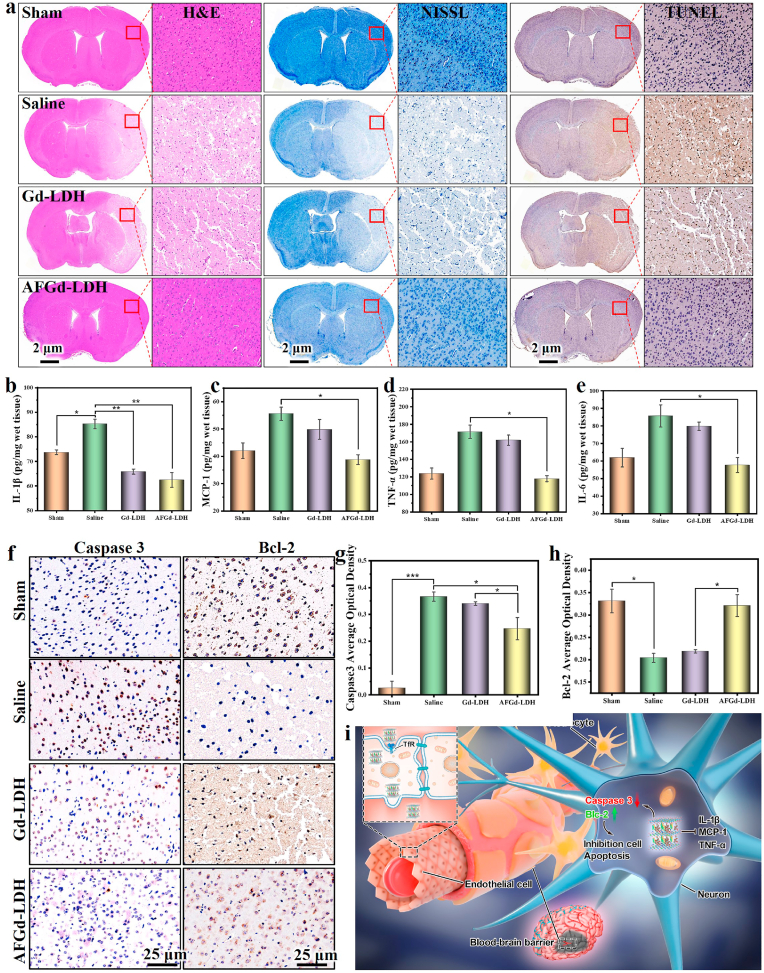
Fig. 5.
Therapeutic effects of AFGd-LDH and its inhibition on inflammation response caused through reperfusion in ischemic stroke. (a) H&E, Nissl and TUNEL staining of brain tissues from various groups. Inflammatory cytokines of IL-1β (b), MCP-1 (c), TNF-α (d),IL-6 (e) in the infarct part of different treatment groups (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. (f–h) The expression level of caspase 3 and Bcl-2 of tMCAO mice from various groups investigated by immunohistochemical staining. (i) Schematic illustration for neuroprotective application mechanisms against reperfusion‒induced injury in ischemic stroke of AFGd-LDH.