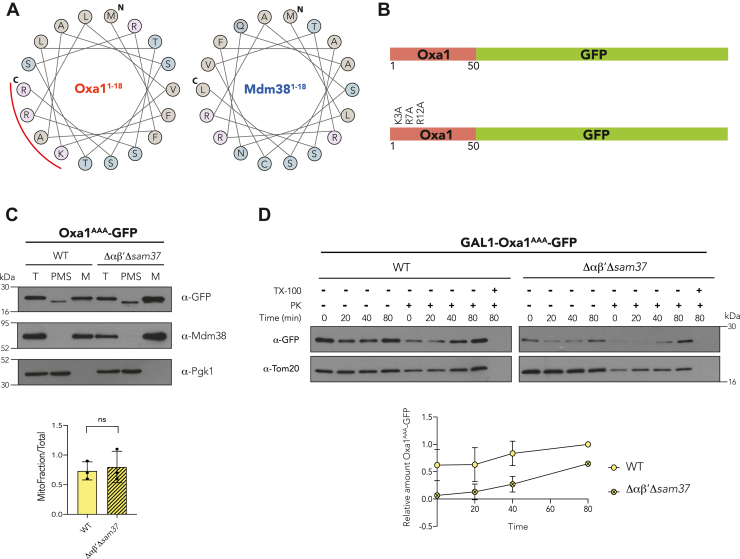
Figure 6.
The Oxa1 first 18 amino acids harbor a cluster of positive amino acids important for αβ′-NAC recognition.A, helical wheel diagram of the first 18 amino acids of Oxa1 and Mdm38: N indicates the first methionine and C indicates the last amino acid of the analyzed sequence; the red curved line shows a positive amino acid cluster found in the Oxa1 MTS. B, schematic representation of the Oxa11–50-GFP construct (up) and the location of the amino acid residues that were changed for alanines (K3A, R7A, and R12A). C, mitochondria were purified from a WT strain or a mutant lacking αβ′-NAC and SAM37 (Δαβ′Δsam37), transformed with the Oxa1AAA-GFP construct plasmid, and the presence of the chimeric protein within the organelle or in the postmitochondrial supernatant (PMS) was analyzed by Western blotting. Endogenous Mdm38 was used as mitochondrial marker and Pgk1 as cytosolic marker. The signals were quantified, and the amount of the corresponding chimera found in mitochondria was compared with the total fraction (T). D, import kinetics of Oxa1AAA-GFP followed in semipermeabilized cells of a WT or a Δαβ′Δsam37 as for Figure 4. MTS, matrix-targeting sequence; NAC, nascent polypeptide–associated complex.