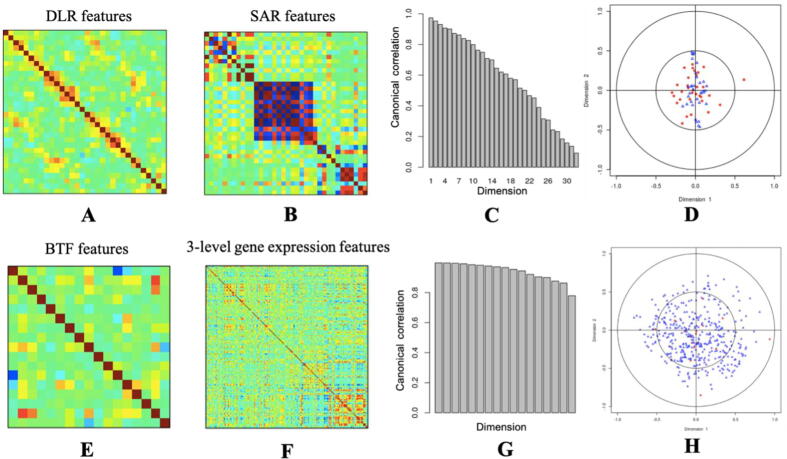
Fig. 5.
The radiomic feature correlation analysis and genomic feature correlation analysis. A: The pairwise DLR feature correlations. Columns and rows are 32 DLR features. The darker colors represent the higher correlations. B: The pairwise SAR feature correlations. Columns and rows are 36 SAR features. The darker colors represent the higher correlations. As we can see, some of the SAR features are correlated with each other. C: The canonical correlations of the two radiomic feature matrices (DLR and SAR). The x-axis is the canonical dimensions, while the y-axis is the correlation of the correlations between the DLR features and SAR features in each dimension. It is telling us, these two feature matrices are highly correlated with each other, which also means, the DLR features are able to capture the majority of information that the SAR features captured. D: The scalar plot of the first two dimensions of DLR features and SAR features. Blue ones are the SAR features, while red ones are the DLR features. DLR features may capture more information than the SAR features because the red dots are more widely spread. E: The pairwise BTF multi-genomics feature correlations. Columns and rows are 17 BTF features. The darker colors represent the higher correlations. F: The pairwise three-level gene expression feature correlations. Columns and rows are 197 (risk gene expressions) + 182 (pathway activities) + 6 (gene signatures) = 385 gene expression features. The darker colors represent the higher correlations. According to the results, we could see that BTF features are more independent than the baseline three-level gene expression features. G: The canonical correlations of the two genomic feature matrices (BTF and three-level gene expression features). The x-axis is the canonical dimensions, while the y-axis is the correlation of the correlations between the BTF features and three-level gene expression features in each dimension. H: The scalar plot of the first two dimensions of BTF features and three-level gene expression features. Blue ones are the three-level gene expression features, while red ones are the BTF features. The BTF feature matrix and the three-level gene expression feature matrix are highly correlated with each other, which also means, the BTF features are able to capture the majority of information that the three-level gene expression features captured. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)