FIGURE 5.
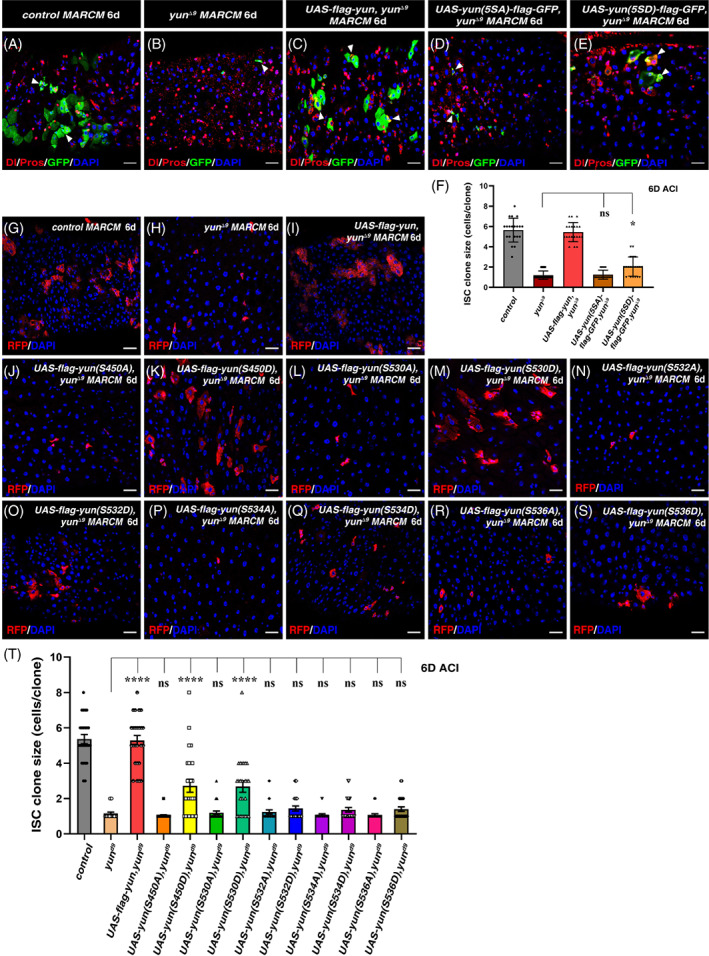
The phosphorylation of the five serine sites in Yun is collectively required for ISC proliferation. (A) MARCM clones of FRT control (green, ACI 6 days), Dl and Pros are in red. (B) The clone size of yun Δ9 is significantly decreased (green, ACI 6 days). (C) Overexpressing Yun can rescue the clone size of yun Δ9 (green, ACI 6 days). (D) Expression of yun(5SA) mutant cannot rescue the proliferation defects observed in yun Δ9 (green, ACI 6d). (E) Expression of yun(5SD) mutant partially rescues the proliferation defects observed in yun Δ9 (green, ACI 6 days). (F) Quantification of the clone size of indicated genotypes. Mean ± SD is shown. n = 20. ns p >0.05; *p < 0.05. (G) MARCM clones of FRT control (red, ACI 6 days). (H) The clone size of yun Δ9 is significantly decreased (red, ACI 6 days). (I) Overexpressing yun can rescue the clone size of yun Δ9 (red, ACI 6 days). (J, L, N, P, and R) Expression of different single phospho‐dead point mutants of yun(1SA) cannot rescue the proliferation defects observed in yun Δ9 (red, ACI 6 days). (K, M, O, Q, and S) Expression of different single phospho‐mimic point mutants of yun(1SD) partially rescue the proliferation defects observed in yun Δ9 (red, ACI 6 days). (T) Quantification of the clone size of indicated genotypes. Mean ± SD is shown. n ≥ 20. ns p >0.05; ****p < 0.0001. In all panels except graphs, GFP is in green and blue indicates DAPI staining of DNA. Scale bars: 20 μm
