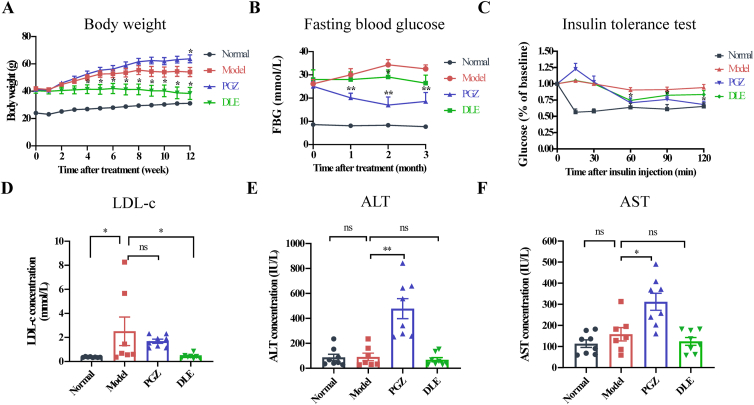
Figure 1.
DLE improved glucose and lipid metabolism-related parameters in db/db mice. (A) The body weight and (B) FBG level (mice were fasted for 6 h) of C57BL/6J mice treated with saline (normal group, black) and db/db mice treated with saline (model group, red), DLE (DLE group, 200 mg/kg, green), or PGZ (PGZ group, 20 mg/kg, blue). (C) Insulin tolerance test. Mice were fasted for 6 h, followed by intraperitoneal injection of insulin (0.6 U/kg). Mouse blood glucose was detected every 30 min for 2 h. (D) LDL-c concentration, (E) ALT concentration, and (F) AST concentration in mouse plasma samples at the endpoint (drug treatment for 12 weeks). The food intake, water intake, FBG increment, TC, HDL-c, and TG in each group are shown in Fig. S1. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 7 for model group, n = 8 for normal, DLE, and PGZ group). Statistical analyses were conducted using Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 vs. the model group, ns means not significant. DLE, Dendrocalamus latiflorus leaf extract; FBG, fasting blood glucose; PGZ, pioglitazone; LDL-c, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase.