Figure 3. . Anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies mechanisms of action.
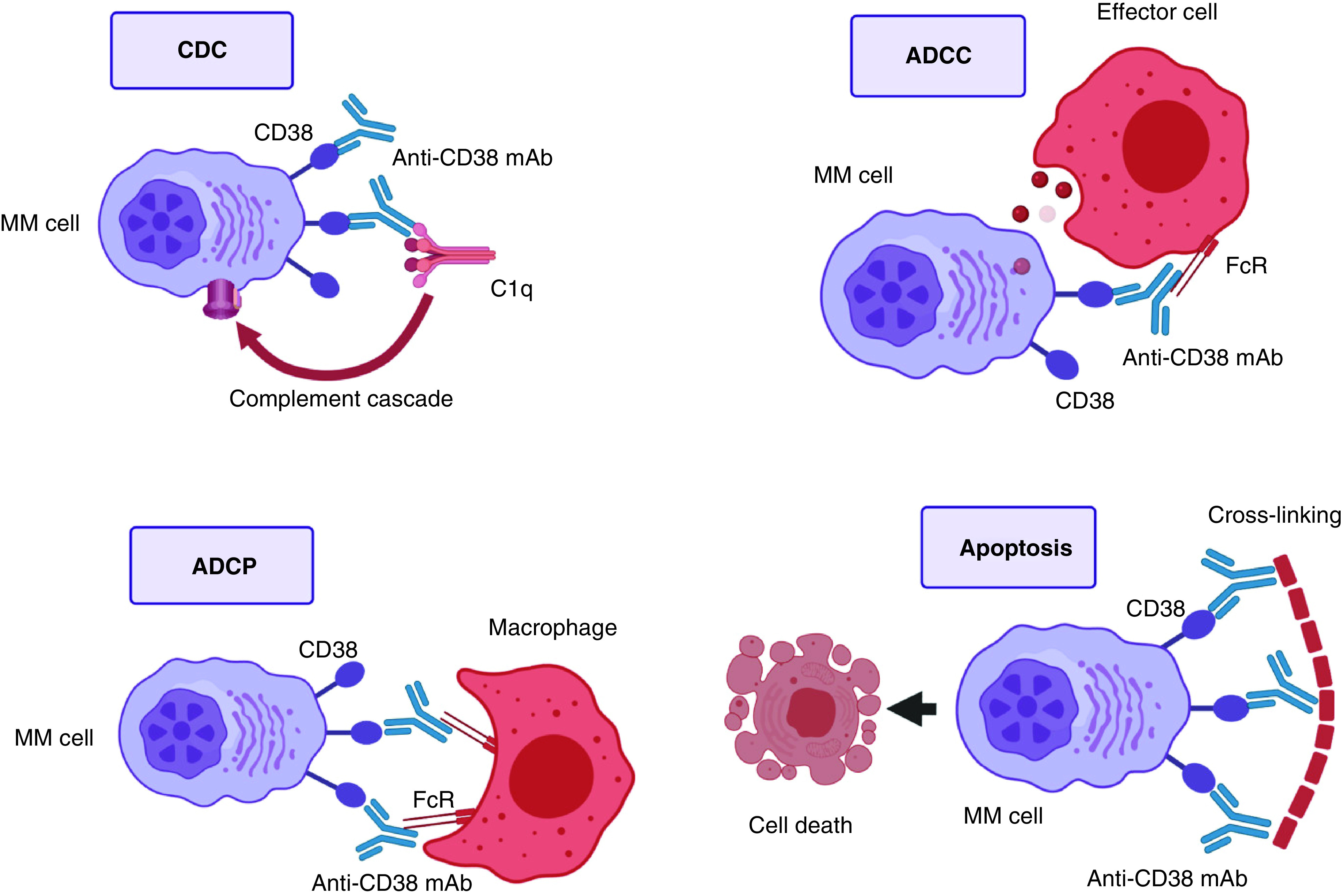
Top left: mAbs bind CD38. The Fc fragment is bound by C1q, initiating the complement cascade, and resulting in a membrane attack complex, leading to cell lysis and death. Top right: mAbs bind CD38. The Fc fragment is then bound by an FcR-bearing effector cell, such as a natural killer cell, leading to activation of cytotoxic processes. Bottom left: mAbs bind CD38, and its Fc fragment is then bound by an FcR-bearing macrophage, inducing phagocytosis. Bottom right: FcR-mediated crosslinking of mAbs induces direct cellular apoptosis.
ADCC: Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; ADCP: Antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis; CDC: Complement-dependent cytotoxicity; MAC: Membrane attack complex; MM: Multiple myeloma.
